6s Orbital Radial Wave Function

Color Online Overlap Of Radial Wave Functions Of Au 11 For Transitions Download Scientific Diagram

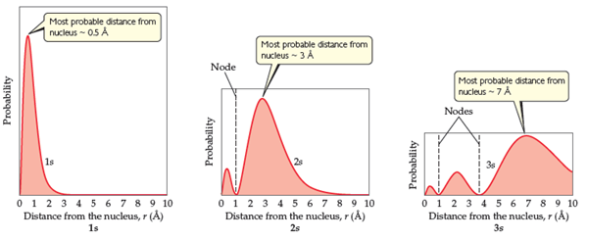
Hydrogen Atom Radial Probability Density Function Hydrogen Atom

Solved 6 Atomic And Molecular Orbitals E G C 2p Or Th Chegg Com
What Is The Value Of The Principal Quantum Number N For The Hydrogen S Orbital Matching These Curves Socratic

Atomic Orbital Chemistrygod

Chapter 2 Section 2 4 Open Inorganic Chemistry
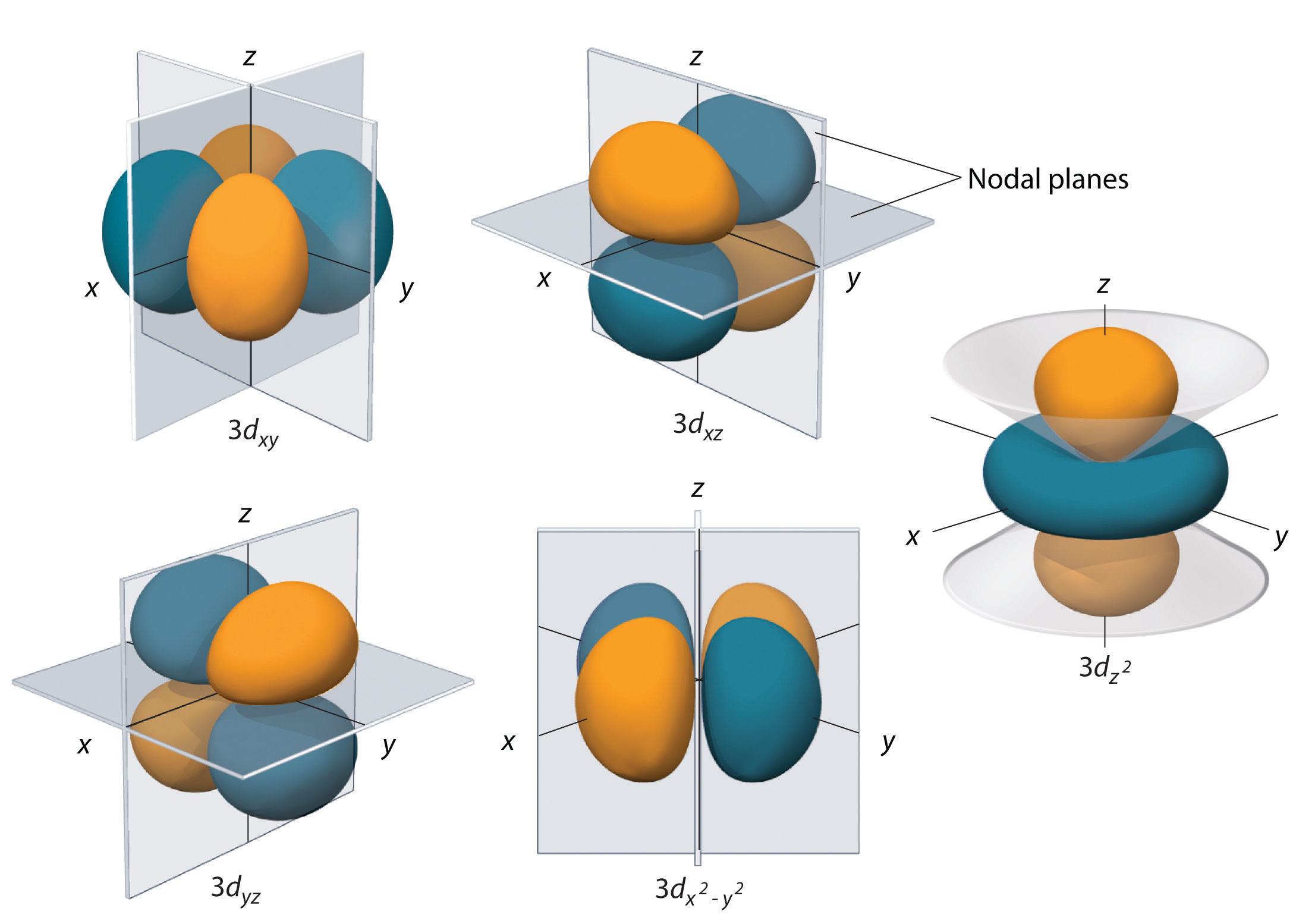
A wave function for an electron in an atom is called an atomic orbital;.

6s orbital radial wave function. Notice that the radial wave function has a prefactor of r2 in the numerator, while the spherical harmonic has a factor of r2 in the denominator, the two of which cancel each other. For which of the following orbital wave function does not change its sign at any distance from the nucleus?. In general, wavefunctions depend on both time and position.
The sign of the wave function makes no difference whatsoever. C)graph the radial distribution function for this system. You square that value.
The 6° angle uses up to 80% less force than a press and creates approximately a 10% sideload. To answer your last question, radial nodes are places where the wave function is zero meaning that the probability of finding an election in those spots is zero. Each script should contain all necessary functions.
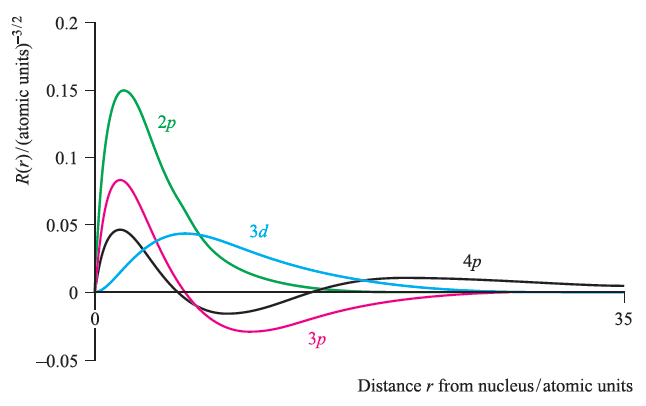
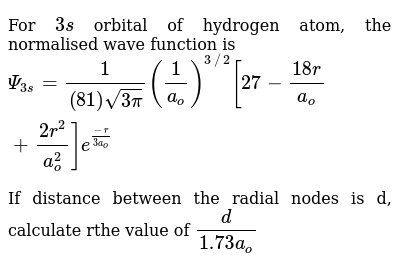
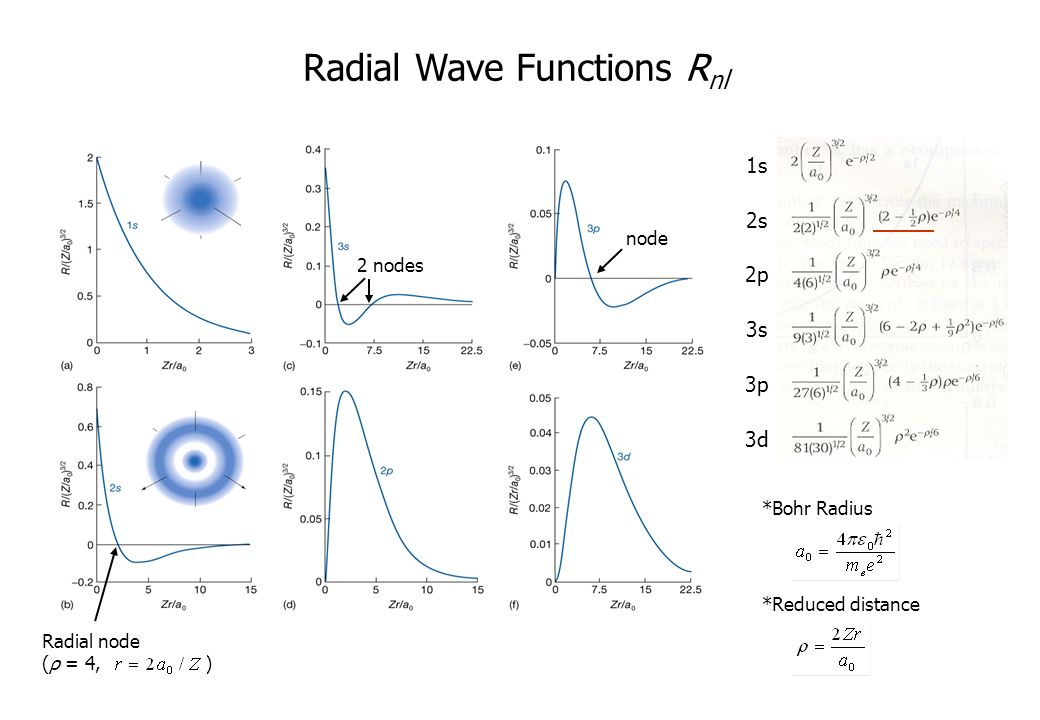
A radial node occurs when the radial function equals zero other than at \(r = 0\) or \(r = ∞\). 3 Radial Plots of the 3s Orbital-0.2 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2 0 5 10 15 0.00 0.05. D orbitals – wave functions • Five d orbitals for each value of n (n 3) l = 2 , m l = -2, -1, 0, 1, 2 • Wave functions slightly more complicated – Radial wave functions same for all 3d orbital • Max probability at r = 9 a 0 • AOs with no nodes have max probabilty at same radius as Bohr model • 4d orbital has 1 node 2 ( 2) 2 3 0 9.
So the wave function does not tell you where the electron's gonna be. The wave function (Ψ) of 2 s is given by Ψ 2 s = 2 2 π 1 ( a 0 1 ) 1 / 2 { 2 − a 0 r } e − r / 2 a 0 At r = r 0 , radial node is formed. This function can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron of an atom in any specific region around the atom's nucleus.The term atomic orbital may also refer to the physical region or space where the electron can be.
Radial Plots of the 1s Orbital Angular Plot Angular Probability Plot Electron Density (Contour) Plot 1s 2s 3s 4s 5s 6s. Blue represents regions within which the wave function is negative and red represents regions where the wave function is positive. Please label & draw the radial parts of the radial distribution functions and wave function regarding the 1s orbital and 8f orbital.
With orbital riveting, the peen is held at a fixed angle, typically 6°, and rotates over the fastener in a circular motion. This behavior reveals the presence of a radial node in the function. Homework Equations using quantum numbers of n=2 l=0 ml=0 ms=+/- (1/2) Z = 1.
So even at points down here where the wave function has a negative value, I mean you can't have a negative probability. In atomic theory and quantum mechanics, an atomic orbital is a mathematical function describing the location and wave-like behavior of an electron in an atom. The wavefunction is ideally a complex quantity whose real part can be negative.
They are the quantum numbers. The graphs below show the radial wave functions. The radial wave function is only dependent on n and l, while the angular wavefunction is only dependent on l and m l.
Just to clear the other questions if there are any:. A radial node occurs when the radial function equals zero other than at \(r = 0\) or \(r = ∞\). The valence electron of which one of the following metals does this wave function correspond to:.
Penetration and shielding are terms used when discussing atomic orbitals (i) Explain what the terms penetration and shielding mean. Radial riveting is quite different. Thus for 2 s, r 0 in terms of a 0 is:.
The origin of the spherical nodes becomes clearer upon examining the wave equation for this orbital. Is a mathematical function that relates the location of an electron at a given point in space (identified by x, y, and z coordinates) to the amplitude of its wave, which. The function of radial wave of a hydrogen atom contains the principal quantum number ( ) and the orbital quantum number (ℓ).
Electron density = ψ 4s 2:. Option 2 2r 0 = a 0. Wave Equation Where H is the Hamiltonian operator:.
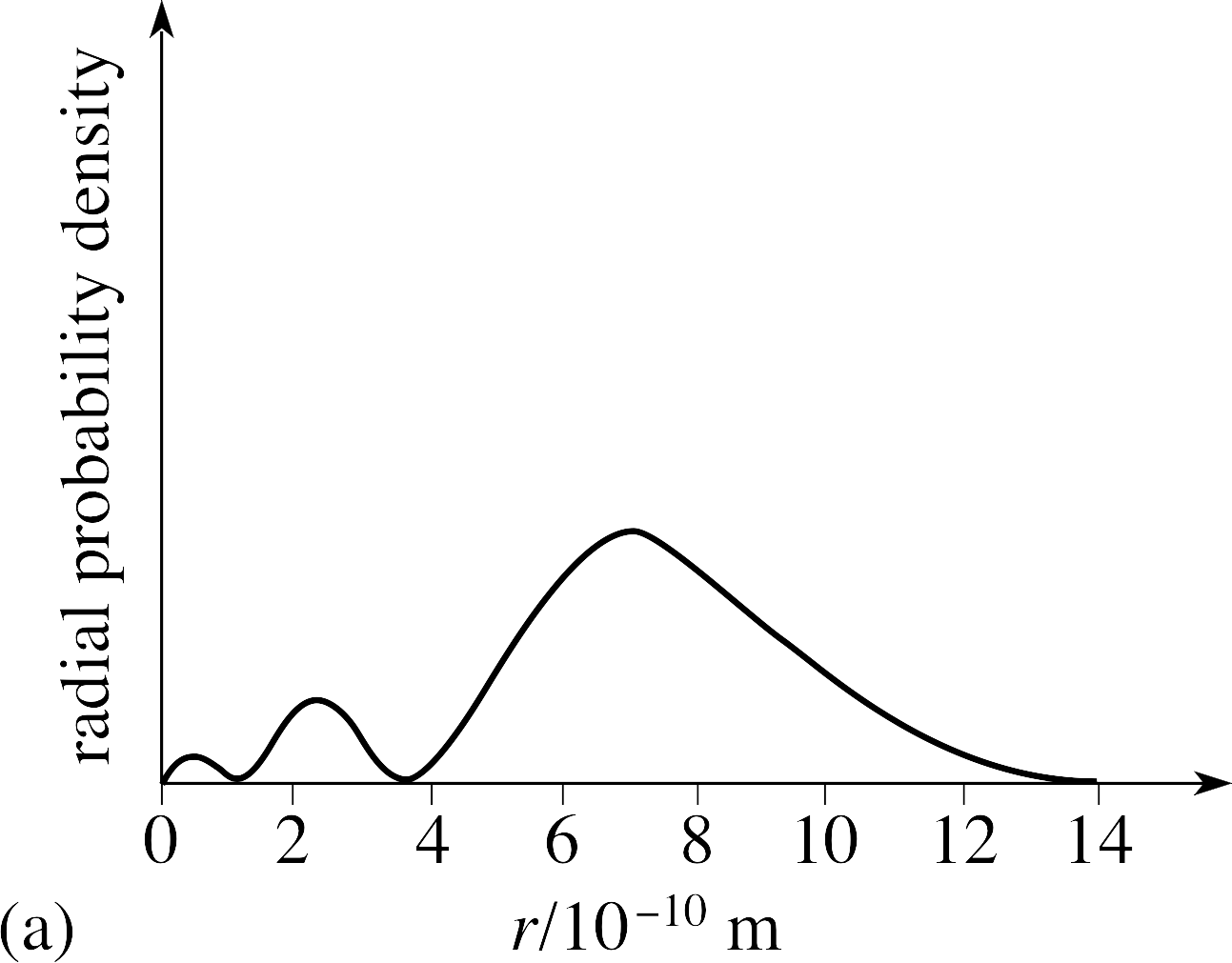
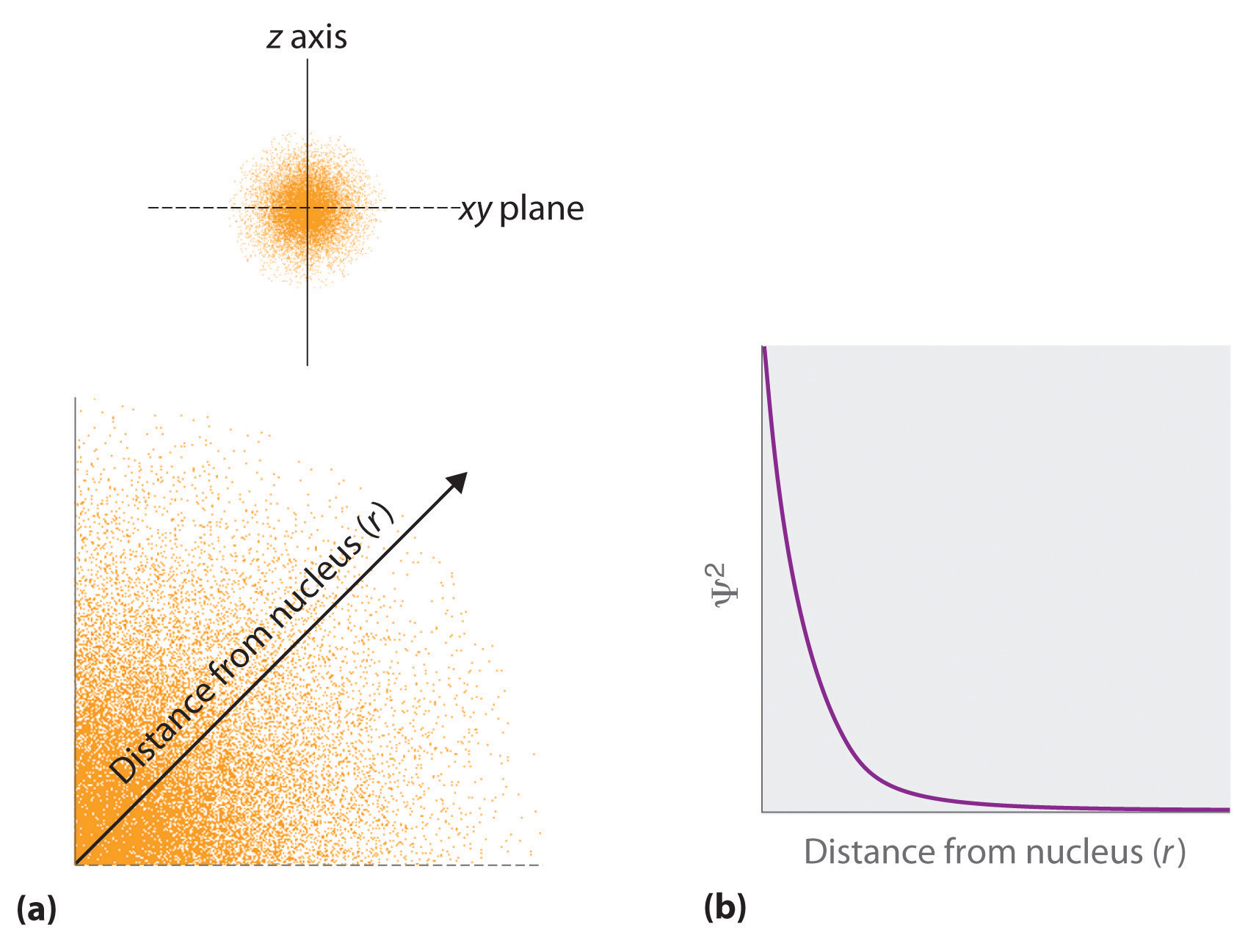
The function of radial wave of a hydrogen atom expresses the movement of electron in a hydrogen atom which propagates spread from the centre of the atom towards all directions and depends on the distance (𝓇) of origin. Another important distinction is that in three-dimensional space, the maximum probability density occurs at the location of the nucleus and not at the Bohr radius, whereas the radial probability density peaks at the Bohr radius. The expected radial distance is 1.5 times the Bohr radius, as a result of the long tail of the radial wave function.
Which Of These May Be Described As 2.3 How Many Orbitals Are Possible For N = 42.4 How Many Radial Nodes Do 3s,. A)Write Complete wave function for an electron in a 2s orbital of hydrogen b)find the probability that the electron is at a distance from the nucleus that is outside the radius of the node. For 4S and 4d orbitals a.
Option 1 r 0 = 2a 0. It just gives you the probability, and technically the square of it gives you the probability of finding the electron somewhere. Next notice how the radial function for the 2s orbital, Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\), goes to zero and becomes negative.
A wave function in quantum physics is a mathematical description of the quantum state of an isolated quantum system.The wave function is a complex-valued probability amplitude, and the probabilities for the possible results of measurements made on the system can be derived from it.The most common symbols for a wave function are the Greek letters ψ and Ψ (lower-case and capital psi. Normalized Wave Functions for Hydrogen Atom p orbitals Quantum numbers n ℓ mℓ 2 1 0 2 1 ±1 3 1 0 3 1 ±1. Erwin Schrodinger published the wave function #psi#, which describes the state of a quantum mechanical system.
(26 of 40) Radial Probability Density Function:. So a particular orbital solution can be written as:. Radial Functions Radial Functions R(r), with σ = Zra0 TABLE 2.4 R(r) Orbital 15 0 2 ao Z 13/2 2a0 2s 2s= 2p R2p 23 2ao 0 (27-180 + 2σ2Je-013 1 2z13/2 81V3 Lao 3p 2213/2 3d R3d81 R3,-- 81 V15 Lao.
Radial distribution function = 4πr 2 ψ 4s 2. They specify what orbitals the wave functions describe. These should suffice for most basic users simply looking for a visualization of orbitals.
For any atom there is just one 6s orbital. Radial probability wave function Contour map of electron density Attach File Browse My Computer Browse Content Collection QUESTION 2 Sketch the wave function for particle in one-dimension box with n=3 and n= 4. The Schrodinger equation is transformed into the Radial equation for the Hydrogen atom:.
Schematic plot of the 6s radial distribution function 4πr2ψ6s2. I have to guess lots of things. Radial wave function, R 4s = (1/96) × (24 - 36ρ + 12ρ 2 - ρ 3) × Z 3/2 × e-ρ/2:.
For s -orbitals, the radial distribution function is given by multiplying the electron density by 4π r2. The wave function psi_(nlm_l)(r,theta,phi) = R_(nl)(r)Y_(l)^(m_l)(theta,phi) for the hydrogen atom describes the state of its atomic orbitals, and require the use of quantum numbers to describe which one we refer to. Probability density of finding a particle.
The wave function of 2s orbital is given by At r r0 radial node is formed Which of the following is correct. (i) the radial wave function (ii) the radial distribution (iii) the angular wave function 4. Boundary surface diagrams of the constant probability density for different atomic orbitals provides a good representation of the shapes of the atomic.
Table of equations for the 4s orbital. PlotHydrogenMolecularOrbital.m by default plots a 3d_z^2 orbital. That on the right is sliced in half to show that there are five spherical nodes in the 6s orbital.
Michel van Biezen ,262 views. Hydrogen Atom Wave Functions:. The Si Problems Gerade?.
L = angular node (another word would be planar) total nodes = (n - 1). At r = r 0 , radial node is formed. 12) The radial probability curve obtained for an orbital wave function has 3 peaks and 2 radial nodes.
Radial wave function b. You could multiply it by math-1/math (or, for that matter, any complex number with modulus math1/math) and nothing meaningful would change. The energy of hydrogen atom in its ground state is.
Get more help from Chegg. Again, for a given the maximum state has no radial excitation, and hence no nodes in the radial wavefunction. Third, that the wave fun.
L = 0, 1, …, n − 1. A better question to ask is, which or. For 3p, it would be (3 - 1 - 1) = 1 radial node.
It is like asking the difference between mass and length!. Second, that you know certainly that the wave function is an eigenfunction of the Hamiltonian operator (stationary state). Please explain why there would be an electron that would go into an empty 1s orbital before going to a 8f orbital.
Radial function Angular function = R(r). H2 2 r2 d dr r2 dR(r) dr + " h2l(l+1) 2 r2 V(r) E # R(r) = 0 The solutions of the radial equation are the Hydrogen atom radial wave-functions, R(r). As it rotates along the tenon, it gently forms the material.
Which of the following is correct?. A wavefunction (Ψ) A mathematical function that relates the location of an electron at a given point in space to the amplitude of its wave, which corresponds to its energy., Ψ is the uppercase Greek letter psi, is a mathematical expression that can be used to calculate any property of an atom. First, that you’re talking about an Hydrogen (or hydrogenoid) atom.
So a positive and a positive wave function create a bonding orbital where the probability of finding an electron is summed while a positive and a negative create an anti-bonding orbital with a lower electron probability in the region between them leading to a repulsion. 2.1 Calculate The R Value In Pm At Which A Radial Node Will Appear For The 2s Orbital Of The Hydrogea Sa 12.2 Which Quantum Numbers Reveal Information About The Shape, Energy, Orientation, And Size 38 2. At r = r 0, radial node is formed.
We also acknowledge previous National Science Foundation support under grant numbers , , and. The LibreTexts libraries are Powered by MindTouch ® and are supported by the Department of Education Open Textbook Pilot Project, the UC Davis Office of the Provost, the UC Davis Library, the California State University Affordable Learning Solutions Program, and Merlot. This behavior reveals the presence of a radial node in the function.
So if we wish to specify a 2p orbital, we pick the wave function with n = 2, l = 1, and some. The electron position r with the Bohr radius a = 1 unit is the distance from the nucleus. A wave function (Ψ) A mathematical function that relates the location of an electron at a given point in space to the amplitude of its wave, which corresponds to its energy.
In this Chemistry video in Hindi for class 11 we explained what is radial probability density in Quantum Mechanics. This is the case with the 2s orbital. H = i˚=2.
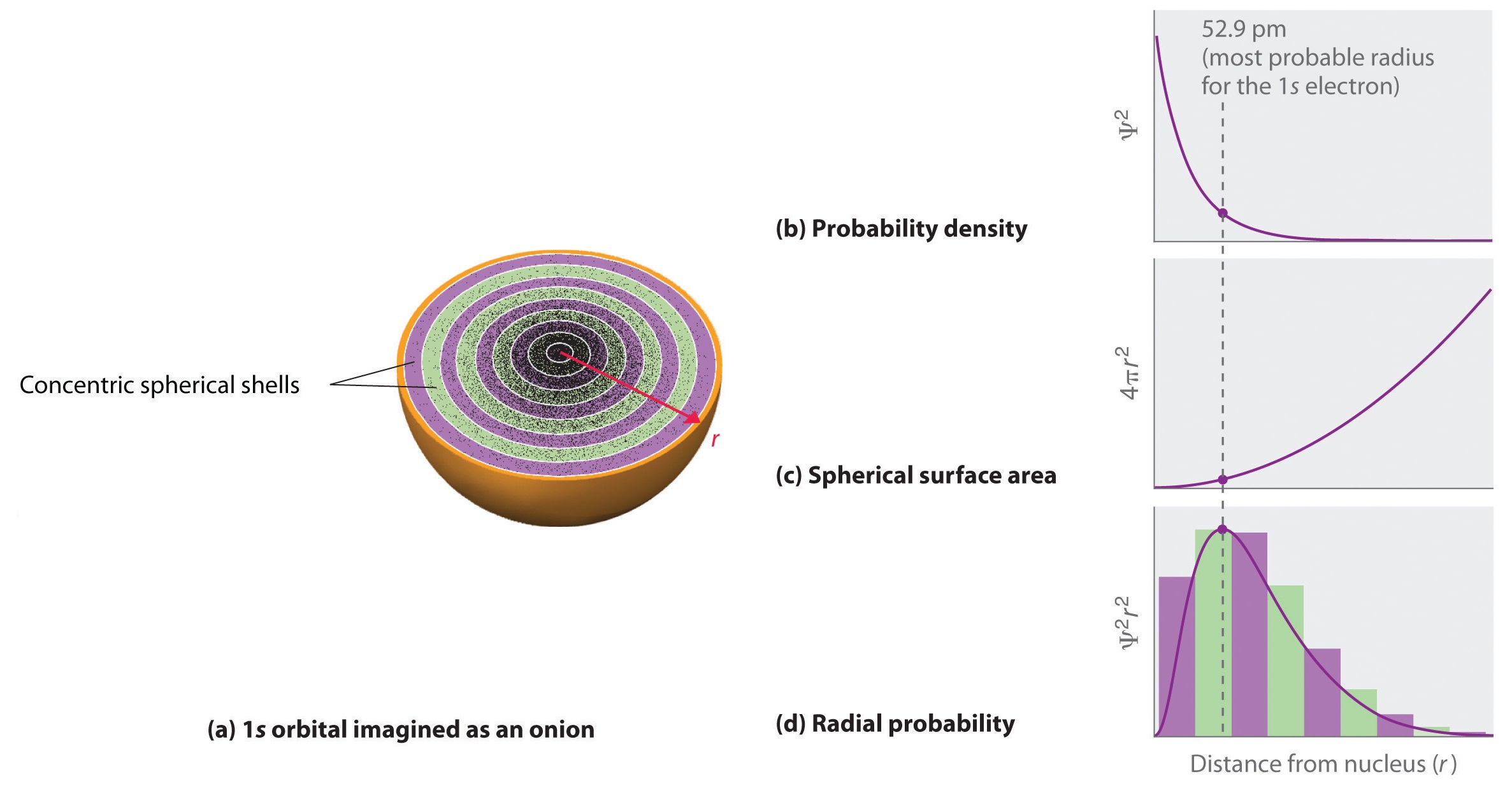
This atomic orbital describes a region of space in which there is a high probability of finding the electron. The image on the left is deceptively simple as the interesting features are buried within the orbital. Show your method (d) For the 2s orbital determine the average radius.
Wave function, ψ 4s = R 4s × Y 4s:. Nodes and limiting behaviors of atomic orbital functions are. Look it up.) (b) For the 2s orbital determine the radial nodes.
You should look at the radial distribution functions above for guidance. As gets smaller for a fixed , we see more radial excitation. Angular wave function, Y 4s = 1 × (1/4π) 1/2:.
For each orbital, its radial density distribution describes the regions with particular probabilities for finding an electron in that particular orbital. Get 1:1 help now from expert Chemistry tutors. However, the modulus or the absolute value of the wavefunction cannot be negative as it has a physical probabilistic interpretati.
M l = − l, …, − 2, − 1, 0, + 1, + 2, …, l. (c) Determine the most probable radius for the 2s. Imagine the bohr atom the electron moves in an orbit (calling it an orbital is not very accurate grammatically) that was earliest quantum theory a full-fledged quantum-mechanical treatment.
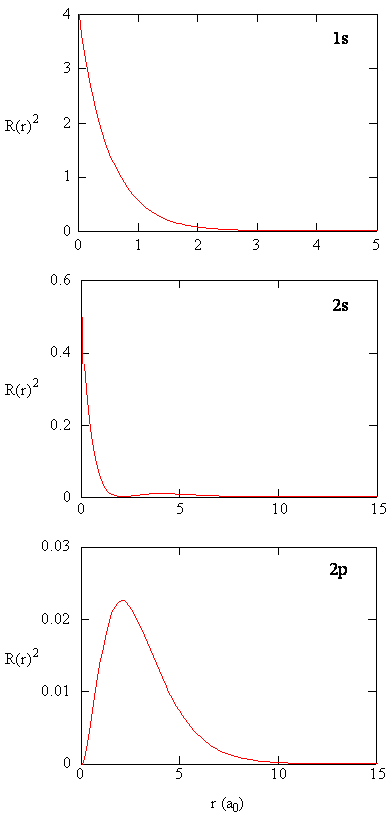
Left, the radial wave function for a 1s (100) atomic orbital of hydrogen plotted as a function of distance from the atomic center. Radial Plots of the 2s Orbital Radial Plot Radial Density Plot Radial Probability Plot. (e) For a 2,1-1 (V.lm) hydrogen orbital, what is L_LHY2,1,1 ( The Ls and H are operators for the hydrogen atom.
The wave function of 2s orbital is given by At r r0 radial node is formed Which of the following is correct. To determine the form of the perturbed wave functions, and resulting real space density away from the +K point ( = +1), we return to the e ective model:. Orbital Wave Function-part 1:Lecture Note 29 Class XI Chemistry Smart Learning.
Energy changes within an atom are the result of an electron changing from a wave pattern with one energy to a wave pattern with a different energy (usually. While still spherical, higher s-orbitals (such. The plots of (a) the orbital wave function ψ(r);.
Calculates a table of the electron radial wave functions of hydrogen-like atoms and draws the chart. (b) the variation of probability density ψ 2 (r) as a function of distance r of the electron from the nucleus for 1s and 2s orbitals. Next notice how the radial function for the 2s orbital, Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\), goes to zero and becomes negative.
(ii) How do these concepts help to explain the structure of the periodic table ?. Each file uses PlotHydrogenMolecularOrbital.m to create and plot simple hybrid orbitals along with basic s, p, d, and f orbitals. Radial Wave Functions R(r) for Hydrogen Atom.
Ψ is the uppercase Greek psi. N = 1, 2, 3, …. Solutions and Energies The general solutions of the radial equation are products of an exponential and a.

Problem 6 Atomic And Molecular Orbitals Pianetachimica It

Quantum Number Wikipedia

Atomic Orbitals And Their Representation Can 3 D Computer Graphics Help Conceptual Understanding
2

Atomic Orbital Wikipedia
Http Nanowires Berkeley Edu Teaching 104a 1402 Pdf

Perspective Relativistic Effects The Journal Of Chemical Physics Vol 136 No 15
Atoms And The Periodic Table V The Orbitals Of Hydrogen Atom

Radial Probability Distributions For The 1 Clutch Prep

A The Radial Wave Functions For Pdrth 3pd4sth B The Radial Overlap Download Scientific Diagram
Nanohub Org Resources 5011 Download Zeemansplitting Pdf
6 6 3d Representation Of Orbitals Chemistry Libretexts
Pplato Flap Phys 11 3 Schrodinger S Model Of The Hydrogen Atom
For 3s Orbital Of Hydrogen Atom The Normalised Wave Function Is
Chemistry Tcd Ie Staff People Sd Lectures Mo Lecture Course 2 Pdf
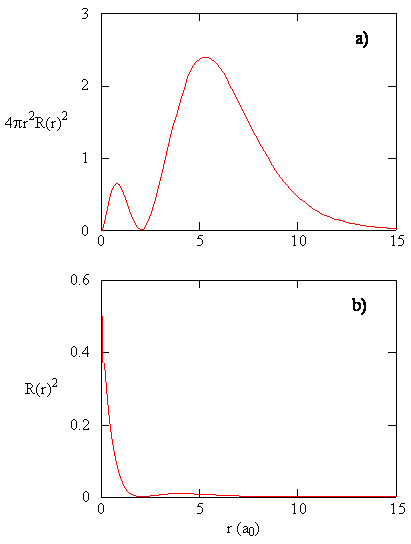
8 2 The Wavefunctions Chemistry Libretexts

Which One Of The Following Represents The 3p Radial Wave Function

A Smooth Path To Plot Hydrogen Atom Via Monte Carlo Method
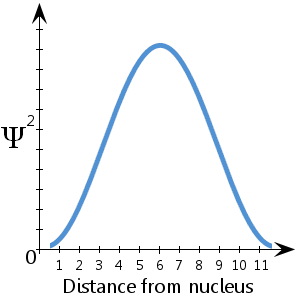
Definition Of Wave Function Chemistry Dictionary
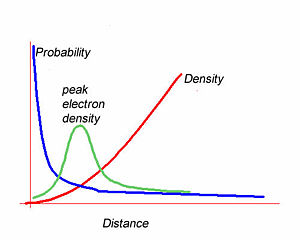
Atomic Orbitals And Nodes Cleanenergywiki
8 1a Interpreting The Radial Probability Distribution Of An Orbital Youtube

Solved I Consider The Radial Wavefunctions For The 4s An Chegg Com
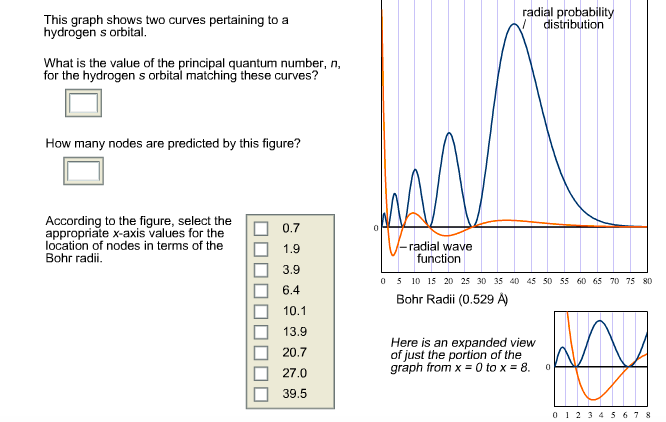
Solved This Graph Shows Two Curves Pertaining To A Hydrog Chegg Com
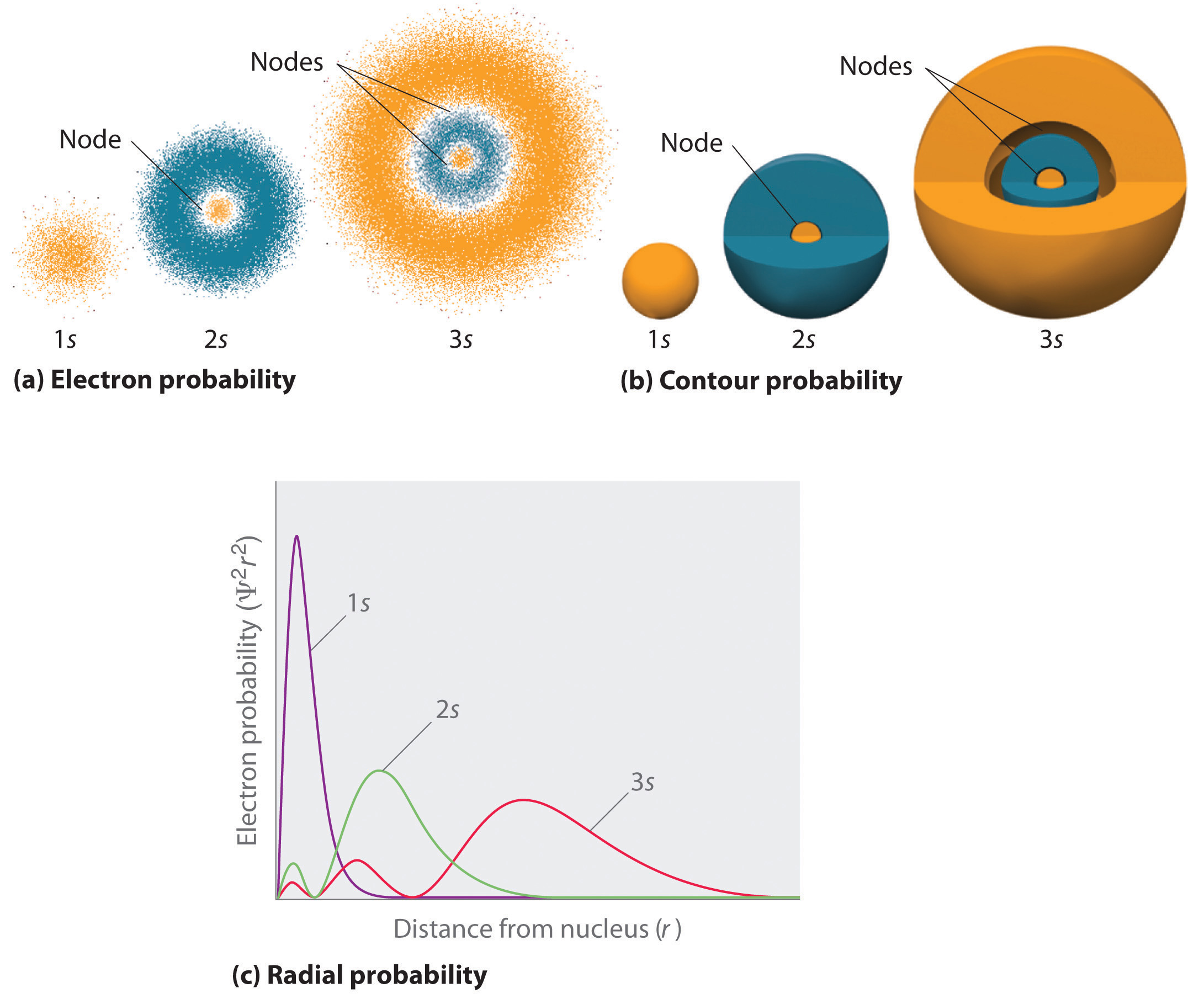
11 10 The Schrodinger Wave Equation For The Hydrogen Atom Chemistry Libretexts
Chemistry Tcd Ie Staff People Sd Lectures Mo Lecture Course 2 Pdf

Radial Probability Distribution Curves Atomic Orbitals

Color Online Angular Averaged Radial Wave Functions R R For The Ni Download Scientific Diagram
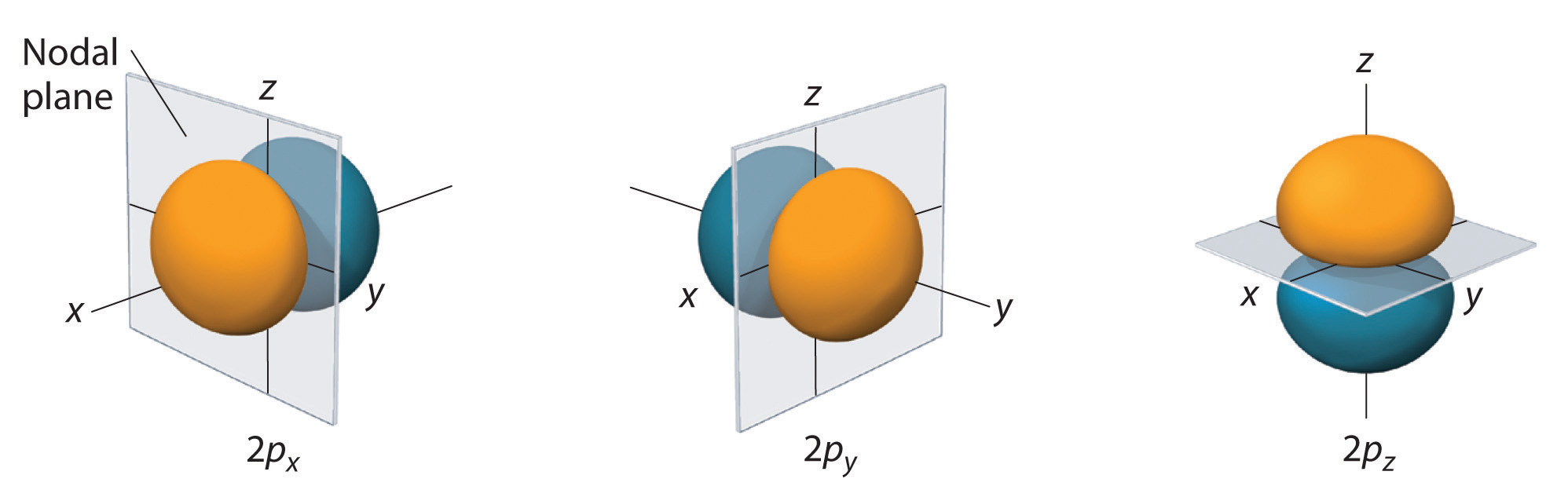
What Do The Subscripts In The Wave Function Psi Nlm L R Theta Phi Indicate Socratic

Chemical Studies Of The Transactinide Elements At Jaea Y Nagame Advanced Science Research Center Japan Atomic Energy Agency Jaea 6th China Japan Joint Ppt Download
Q Tbn 3aand9gcrghga0ooj Vhioszfatpprdyurcdmzptofnputdbx2rits4zr7 Usqp Cau

Atomic Orbital Chemistrygod
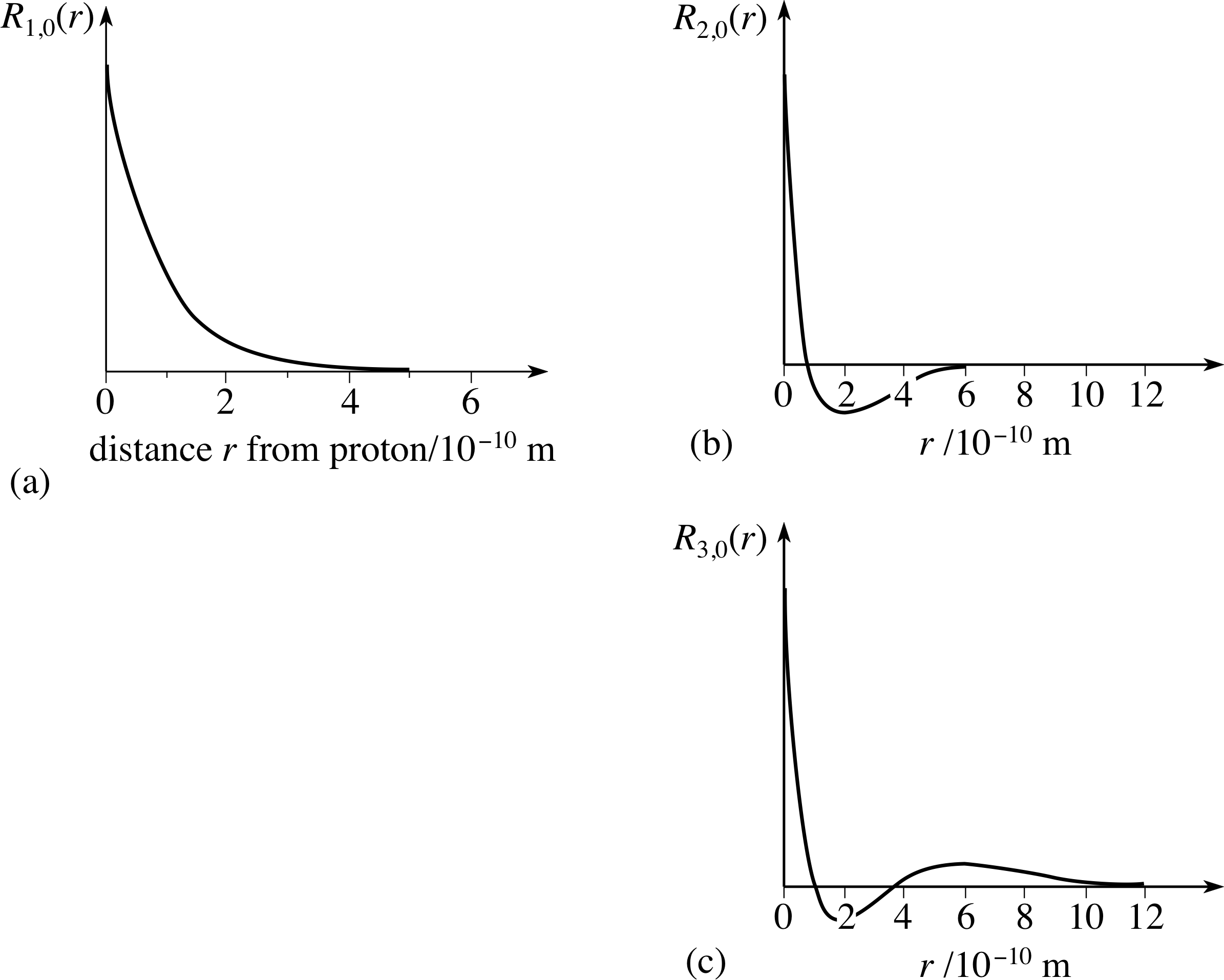
Pplato Flap Phys 11 3 Schrodinger S Model Of The Hydrogen Atom
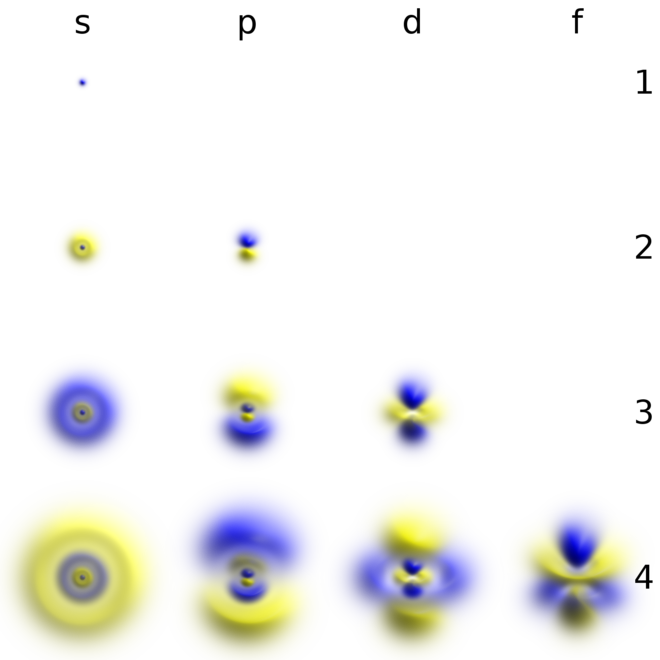
Atomic Orbital Wikiwand
Sharadpra Files Wordpress Com 16 12 Radial Distribution Function Pdf

4f And 5d Radial Distribution Functions Of Ce 3 And The Radial Download Scientific Diagram
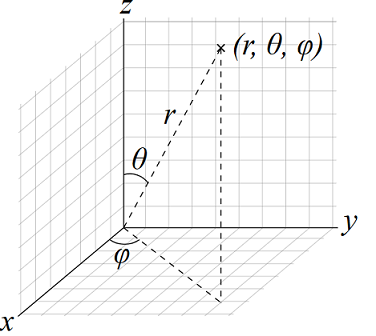
The Wave Function Of An Orbital Of H Atom Is Given By Psi Sqrt Q 81 Sqrt Pi 1 A 0 3 2 6 R A 0 R A 0 E R 3a 0 Sin Theta Sin Phi Then Find The Orbital Socratic

Atomic Orbital Chemistrygod
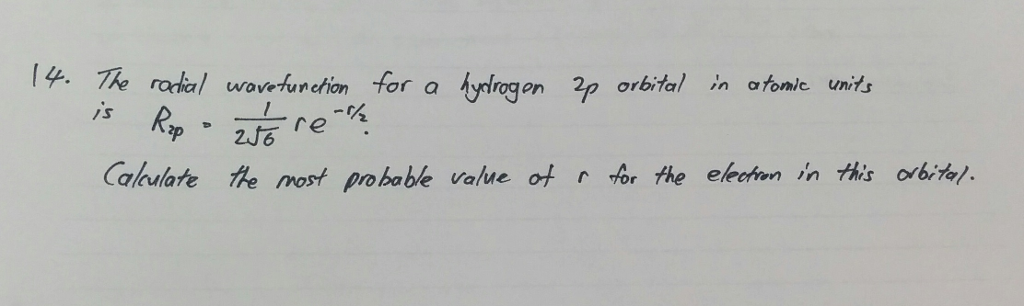
Solved The Radial Wavefunction For A Hydrogen 2p Orbital Chegg Com

Solved 1 The Spherical Harmonic Corresponding To A P Or Chegg Com

Square Of The Radial Wavefunctions For The 4f 5s 5p And 6s Energy Download Scientific Diagram
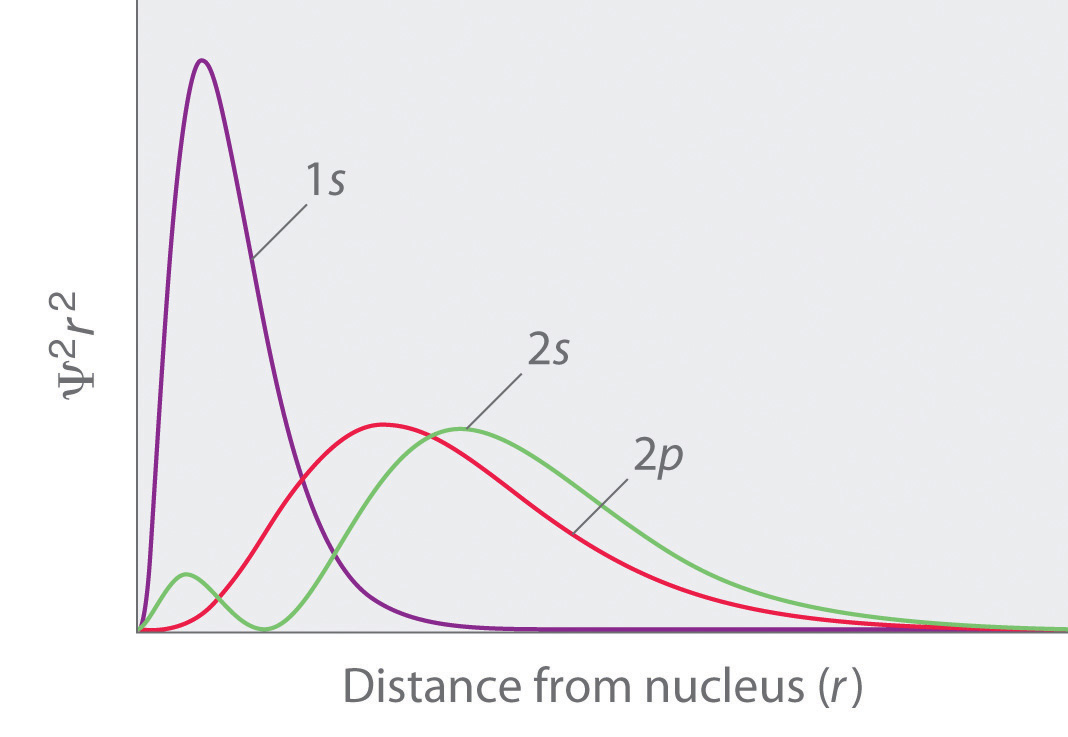
Chapter 2 5 Atomic Orbitals And Their Energies Chemistry Libretexts
Why Is A Complete Octet Or Duplet More Stable Than A Neutral Atom Quora

Solved A Verify That The N L 2 1 Solution R R Chegg Com
Radial Distribution Functions
11 10 The Schrodinger Wave Equation For The Hydrogen Atom Chemistry Libretexts
Lecture 11 Hydrogen Atom References Engel Ch Ppt Download
Pdf4pro Com Cdn Chapter 1 Basic Concepts Atoms 8c3 Pdf

Solved A Two Types Of Nodes Occur In Atomic Orbitals Sp Chegg Com
Solved Consider The Discussion Of Radial Probability Functions Chegg Com

Atomic Orbital Chemistrygod
Http Chemistry Tcd Ie Staff People Sd Lectures Mo Lecture Course 3 Pdf

Atomic Orbital Wikipedia
8 2 The Wavefunctions Chemistry Libretexts

Why Do D And F Electrons Have A Poor Shielding Effect Compared To S And P Electrons Quora
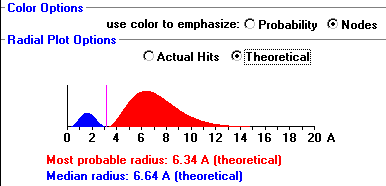
Orbital Exe Help

An Introduction To Molecular Orbital Theory
Q Tbn 3aand9gcrghga0ooj Vhioszfatpprdyurcdmzptofnputdbx2rits4zr7 Usqp Cau
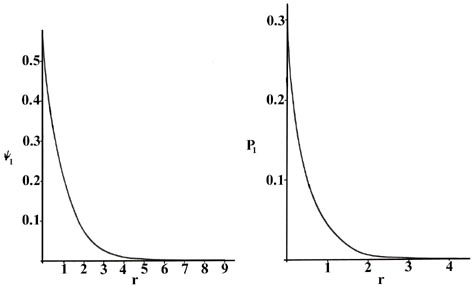
The Hydrogen Atom The Probability Distribution Of The Hydrogen Atom
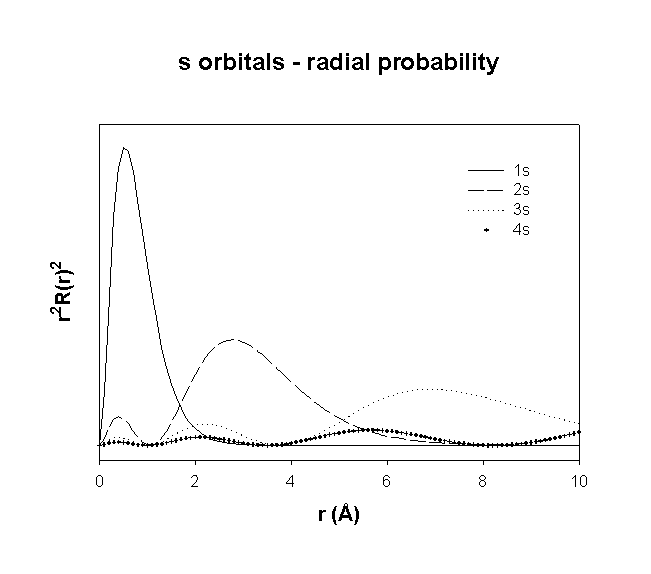
Chm 401 Lecture 1

Upper Radial Component Of The Cs 6s Orbitals Thick Solid Line Download Scientific Diagram

Solved 6 Select An Orbital Of Parameter N 3 A Write The Chegg Com

Text Template
Atomic Orbitals And Their Energies

Hydrogen Like Atom Encyclopedia Article Citizendium

Color Online Overlap Of Radial Wave Functions Of Au 11 For Transitions Download Scientific Diagram

Lanthanide Alkylidene And Imido Complexes Dalton Transactions Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039 Be

Lanthanides Actinides Electronic Properties
Q Tbn 3aand9gcqsfpcl0fvvqnircpzeznjarc6gltkbcwzbj7akc3e Usqp Cau

Radial Probability Distribution Of Hydrogen Atom In Ground State Youtube
Http Nanowires Berkeley Edu Teaching 104a 1402 Pdf

Hydrogen Atom Hydrogen Atom Radial Wave Functions
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq6pcocjmyoorqurs8vizjbtxloj2nxidvntygwlup0ifa9h0wg Usqp Cau
Atomic Orbitals And Their Energies

Quantum Chemistry 7 5 Hydrogen Atomic Orbital Nodes Youtube

11 10 The Schrodinger Wave Equation For The Hydrogen Atom Chemistry Libretexts
Royalsocietypublishing Org Doi Pdf 10 1098 Rspa 1956 0085
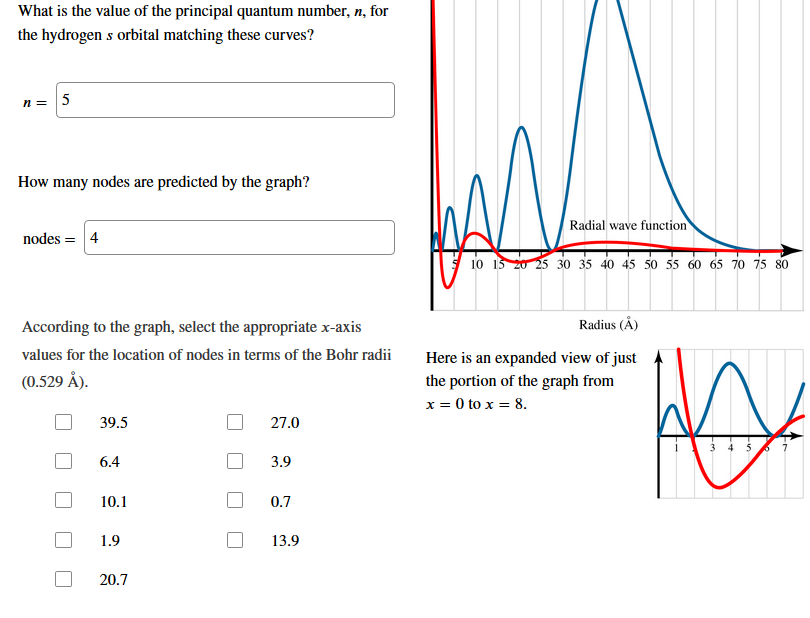
Answered What Is The Value Of The Principal Bartleby

Atomic Orbital Wikipedia
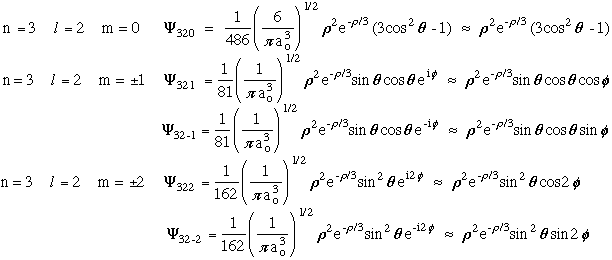
Iii Quantum Mechanics
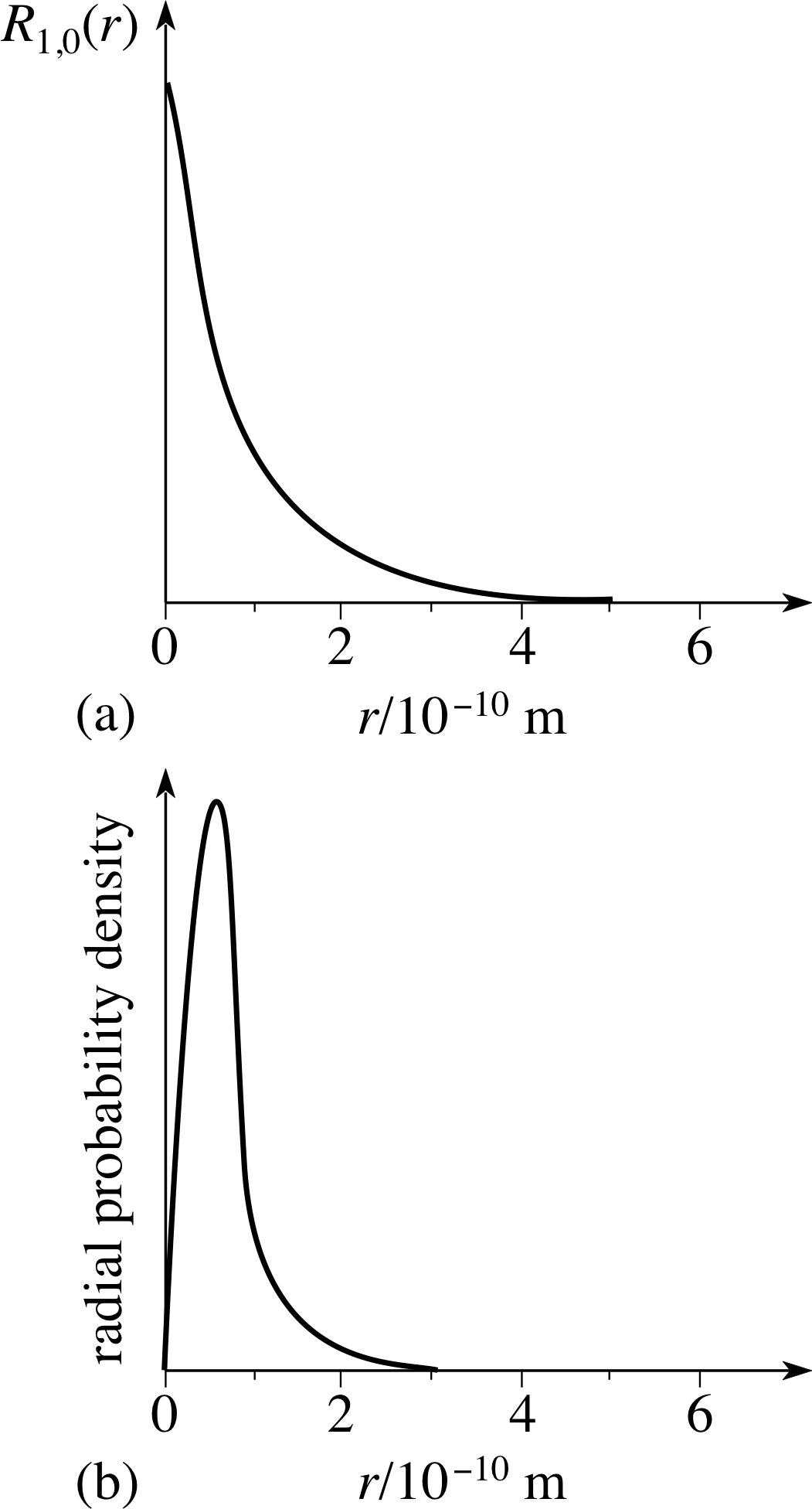
Pplato Flap Phys 11 3 Schrodinger S Model Of The Hydrogen Atom

Why Are The Radial Wavefunction And Radial Distribution Function Different Chemistry Stack Exchange

Radial Probability Distribution Curves Quantum Mechanics Csir Net Gate Chemistry Iit Jee Jam Neet Youtube
Verify That The N L 2 1 Solution R Pho Chegg Com
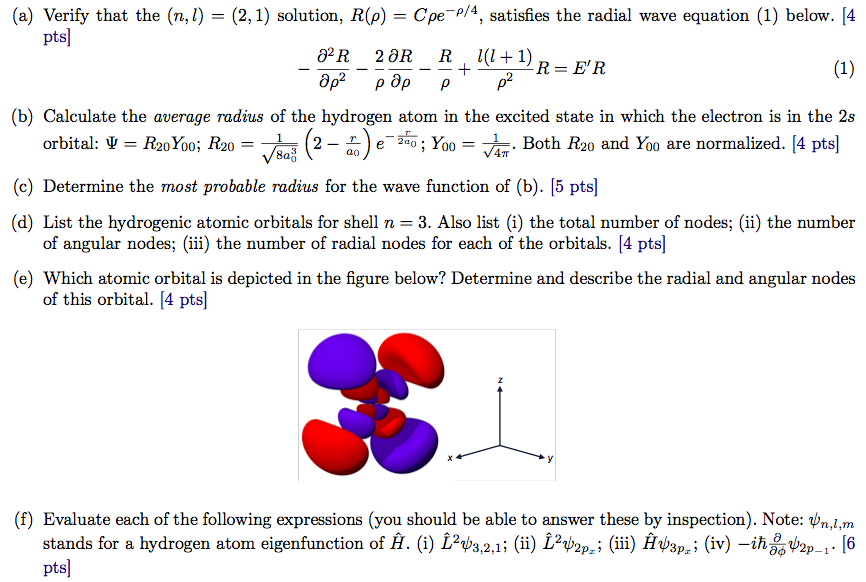
Structural Characterization Of Small Xe Clusters Using Their 5s Correlation Satellite Electron Spectrum Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics Rsc Publishing

Radial Wavefunctions Of The 4f And 5d Orbitals In The Free Pr 3 Ion Download Scientific Diagram
Learn Examples On Radial Probability Distribution Curve Meaning Concepts Formulas Through Study Material Notes Embibe Com
Definition Of Orbital Nodes Chemistry Dictionary

Radial Wave Function For The Neutron 0p 3 2 Natural Orbital Heavy Download Scientific Diagram

The Radial Wave Functions Of Si 2s2p1d Orbitals Download Scientific Diagram
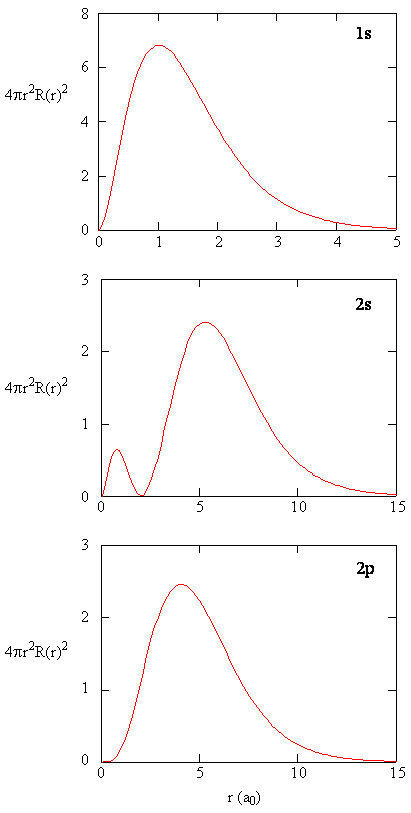
8 2 The Wavefunctions Chemistry Libretexts
Http Nanowires Berkeley Edu Teaching 104a 1402 Pdf

6 7 8 9 Uu R R For Is Orbital Of Hydrogen Atom Radial Wave Function
.PNG)
The Radial Wavefunctions
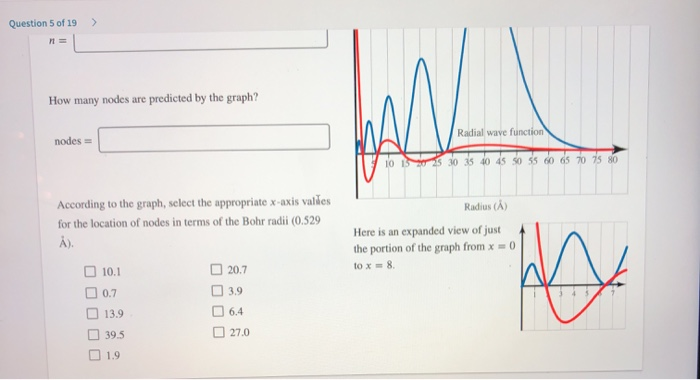
Solved Question 5 Of 19 The Graph Shows Two Curves Pert Chegg Com

The Radial Wavefunction Solutions

Square Of The Radial Wavefunctions For The 4f 5s 5p And 6s Energy Download Scientific Diagram

1 What Is The Ratio Of The Energy Of A Ground To That Of A Ground State Be Ion

Solved 3 For The 3py 5s 3dxy And 4dxz Hydrogen Like Chegg Com



