3d Printing Organs

3d Printed Organs Are A Heartbeat Closer To Reality
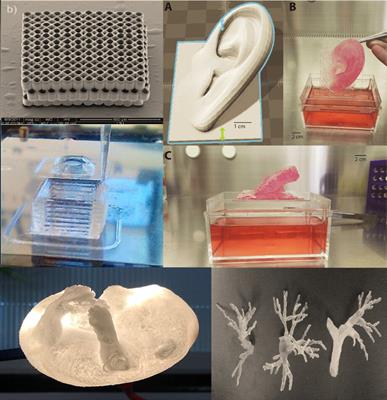
3d Printing For Implantable Medical Devices From Surgical Reconstruction To Tissue Organ Regeneration Frontiers Research Topic
3d Printers Will Soon Be Used To Print Human Organs

What You Need To Know About 3d Printed Organs Engadget
Making Realistic 3d Printed Organs To Plan Surgery Annual Reviews News
1
Further advances and uses are being developed in the healthcare sector providing some of the biggest advances from using the technology.

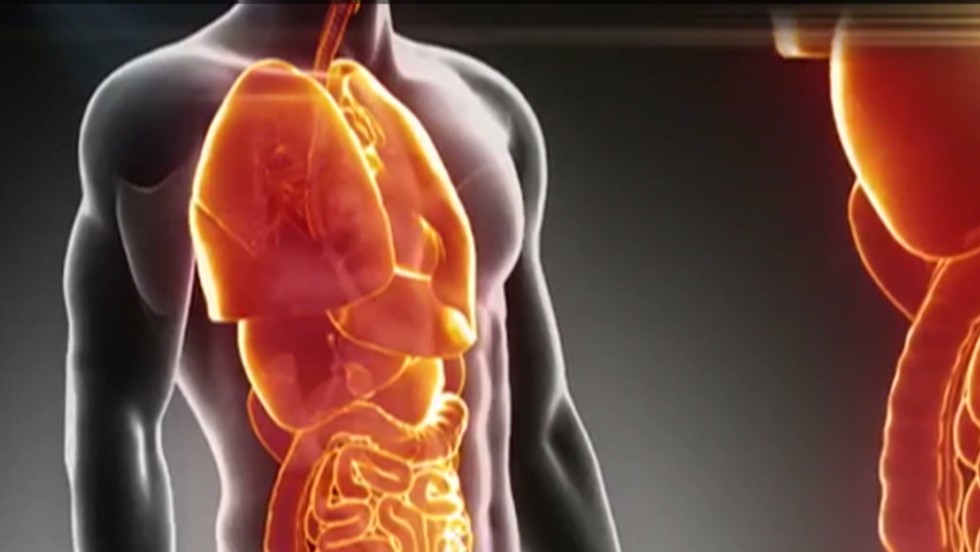
3d printing organs. 3D Printing Tissues and Organs Just Got Faster. We have already progressed in including 3D Printing for bone transplants. The most promising of of 3D printed organs for transplant is the heart.
Subscribe for more tech & culture vide. To put it very simply, the process of 3D organ printing uses the patient’s own tissues. High resolution was a critical requirement for designing intricate capillaries and microcellular.
The process is also called 3D bioprinting because it combines 3D printing like-techniques, cells, and biomaterials to create living tissues. 3D printing of organs (also known as bio-printing) is a process of creating scaffolds, human tissue, and organs in controlled environments by layered deposition of materials. Hence, the implications are already known.
As organs go, the heart is actually one of the easiest to recreate because it doesn’t employ any complex biochemical reactions. There, the usual polymer materials are efficient, but unsuited to printing organs. Reprinting human organs has a number of potential uses.
By comparison, 3D-printing technology offers both greater speed and computer-guided precision in printing living cells layer by layer to make replacement skin, body parts and perhaps eventually. San Diego-based Organovo has been around since 07 and has had some success in printing parts of lung, kidney and heart muscle. As described by the Prellis team in their white paper, there are four parameters to be considered while 3D printing viable human tissues:.
In the near term, tissues and organs grown on such scaffolds might also find use as sophisticated, 3D tissue “chips,” with potential for use in studies to predict whether drugs will be safe in humans. 3D printing organ utilizes the techniques used in conventional 3D printing where a computer model is fed into a printer and produces layers of filament like plastics or wax until it completes a 3D object, in this case, organs like ear, heart, or kidney. However, it is done with the help of titanium, an already tested material for surgeries.
Edd Gent - May 07, 19. Several 3D printers simultaneously create a two-dimensional slice of a tissue or organ, then the pieces are assembled in a. Researchers have also made progress with one of the biggest challenges in printing 3D organs by creating blood vessels or arranging of blood vessels in an organ, also known as vasculature.
The ear transplants are, he says, “kind of the first proof of concept of 3-D printing for medicine.” Researchers have been using 3D-printing techniques in hopes of developing tissues that can be transplanted into humans. 3D printing is not magic. Potentially, the organ waiting list could be erased and people would just print the organ they needed.
EVERY year about 1,000 organs, mostly kidneys, are transplanted from one human being to another. 3D printing is being used in the medical sector to help save lives by printing organs for the human body such as livers, kidneys and hearts. There are several challenges that must be addressed to bioprint fully functional organs using EBB.
Blood vessels are a complicated network and complex, at the same time need to be flexible to pump the blood and keep their tissue functions. Bioprinting can produce living tissue, bone, blood vessels and, potentially, whole organs for use in medical procedures, training and testing. Rather, its primary function is to act as a pump.
In North Carolina researchers at Wake Forest have produced a 3D printer technology that can ‘print’ tissues, organs and bones that can potentially be implanted into a patient. The promise of printing human organs began in 19 when Charles Hull invented stereolithography.This special type of printing relied on a laser to solidify a polymer material extruded from a nozzle. A standard 3-D printer layers plastic to create car parts, for example, or trinkets, but a bioprinter layers cells to form three-dimensional tissues and organs.
3d printing organs for transplant Anyone who hears for the first time about the possibility of organ printing believes that it is merely a joke. The tricky part is the. Ability to 3D bioprint living models could reduce the need for animal models, which would save time, material and money.
Bioprinting is an extension of traditional 3D printing. In fact, organ printing is a process that has already passed the initial planning stage. August 18,.
Much work in regenerative medicine has focused on the idea of creating scaffolds. Doctors or researchers harvest a small subsection of healthy tissue that they then use to expand the cells outside of the body. Faster and more precise than traditional methods of building organs by hand.
At the point in time, we can print the less complex organs like skin and bladders but we still have a lot of advancements to make. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3D printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3D object is produced. In addition to transplants, scientists are using 3D printed organs to better understand how they are affected by cancer.
The average wait time for a transplant is 4 months for a heart, and 5 years for a kidney, according to Gift of Life. Aside from difficulties making a 3D-printed organ's cells behave like the real thing, scientists also find it hard to create blood vessels. »»» Subscribe to The National to watch more videos here:.
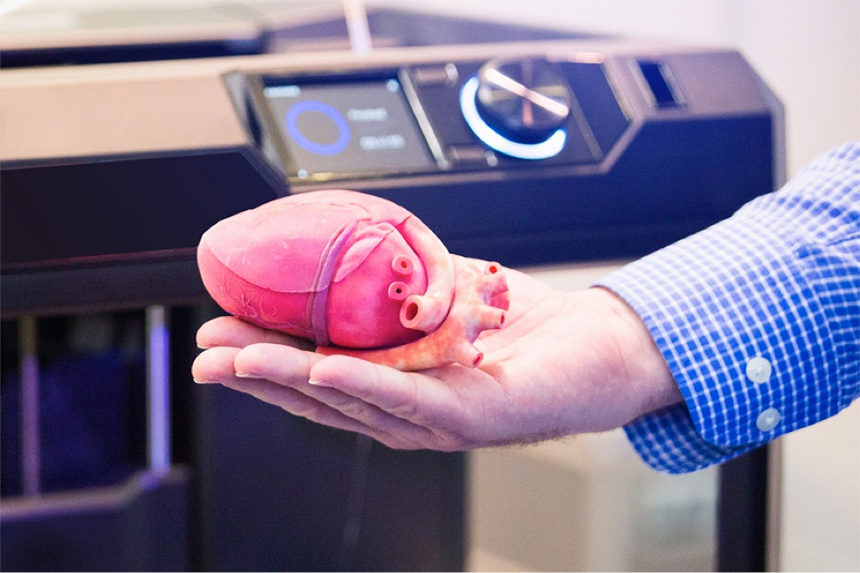
This relatively new field has emerged from several established industries. That’s where 3D printed organs, such as 3D printed hearts, come in. 3D Printing of Organs.
You can find out more of this research that has been published in the scientific journal called Nature Biotechnology. 3D bioprinting claims a host of both benefits and drawbacks. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic.
This area of research aims to use stem cells and other technologies—such as engineered biomaterials—to repair or replace damaged cells, tissues, or organs. In addition, 3D bioprinting has begun to incorporate the printing of scaffolds. 3D-printed hearts with 'beating' tissue could ease organ donor shortage There are more than 1,000 people in the United States waiting for donor organs to become available.
An academic team from the University of the West of England’s Center for Fine Print Research (CFPR) is using 3D printing to produce realistic organs for use in surgical training. 3D Printing & CAD;. 3D-Printed Footwear -30, an Analysis of the Market Potential of 3D Printing in the Footwear Industry.
"The mechanical process isn't all that complicated. However, emerging innovations span from bioprinting of cells or extracellular matrix deposited into a 3D gel layer by layer to produce the desired tissue or organ. Like many 3D printing techniques, 3D stereolithography was originally designed for more traditional manufacturing.
During this time people can become more ill and die, so the ability to print organs using 3D bioprinting would be invaluable. Now researchers have shown that a common food dye could solve the problem. Soon, Your Doctor Could Print a Human Organ on Demand At a laboratory in North Carolina, scientists are working furiously to create a future in which replacement organs come from a machine.
Improved Technique of 3D Printing Viable Human Organs. With a goal of 3D printing patches made of human tissue for defunct organs and entire organs for transplantation, Organovo has a difficult task ahead, but not impossible to pursue. We’re tantalizingly close to growing organs in the lab, but the biggest remaining challenge has been creating the fine networks of blood vessels required to keep them alive.
To overcome the tremendous gap, the study in technology of 3D printing by medical researchers and post close examination, it was seen fir to introduce 3D printed organs. In the future, 3D printing technologies may be used together with advances in stem cell research to print living bone cells from patients' own cells or functioning organs for transplant (such as. 3D printing holds the promise of changing the healthcare industry for the better, offering patients things like smarter drugs, hyper customized prosthetics, and even new organs.
But, in the case of organ transplant, the organ would be derived from the patient’s own cells. In 15, it announced a partnership with the cosmetics behemoth. Those cells are used to produce new tissues and organs that can then be placed back into the bottom.
How 3-D printing is helping to revolutionize organ repair and rebuilding. There have been decades of research into the technology, and companies like BioBots (which made its debut on the. Inkjet technology, optical and electronic applications, additive manufacturing or.
Resolution, speed, complexity, and biocompatibility. New Progress in the Biggest Challenge With 3D Printed Organs. Organ printing involves using 3D printing techniques to create an artificial device for use in an organ replacement operation.
Emerging 3D printed organs projects The biggest challenge of 3D printing organs:. However, all 3D-printed human tissues to date lack the cellular density and organ-level functions required for them to be used in organ repair and replacement. The cellular complexity of the living body has resulted in 3D bioprinting developing more slowly than mainstream 3D printing.
Organs need arteries, veins and capillaries to pump blood. New successes in printing vascular tissue from living cells point to the accelerating pace of development of 3D-printing tissue — and eventually the ability to manufacture organs from small. Our team has successfully engineered bladders, cartilage, skin, urine tubes and vaginas that have been implanted in patients.
After patches were implanted into the mouse’s liver in the Organovo study, blood was supplied to it by the surrounding liver tissue. In extrusion-based bioprinting (EBB), bioink is dispensed from a printing chamber out of a printing nozzle. What keeps the organs working are blood vessels and they are the hardest to reproduce.
In the long term, this technology may allow production of replacement organs from those needing them. Some printed tissues, such as skin and bone, are already being tested in humans, while many others are early in development. As with any industry in its infancy, standard practices are still evolving, and the hurdles faced in growing 3D tissues and organs are the subjects of exciting research all over the world.
These patient-specific organ models, which include 3D-printed soft sensor arrays integrated into the structure, are fabricated using specialized inks and a customized 3D printing process. Currently, bioprinting can be used to print tissues and organs to help research drugs and pills. Prellis isn’t the first company to develop three-dimensional organ printing.
Proponents of the technology endorse the efficiency and ease of the printing process, while others condemn the printers as ethically provocative and inaccessible to the general masses. Transplantation of printed organs has recently been made on different laboratory animals. Bioengineers at Rice University created entangled cardiovascular networks similar to the body’s natural passageways.
Still, an entire organ would need to be prepared for blood flow. Artificially grown human organs are seen by many as the “holy grail” for resolving this organ shortage, and advances in 3D printing have led to a boom in using that technique to build living tissue constructs in the shape of human organs. And while printing whole human organs for surgical transplants is still years away, the technology is rapidly developing.
Advances in 3D printing techniques have led to hope for improvements in regenerative medicine. It is simply a way to scale up the current processes we use to engineer organs in the laboratory.

Wake Forest Researchers Successfully Implant Living Functional 3d Printed Human Tissue Into Animals 3dprint Com The Voice Of 3d Printing Additive Manufacturing
Your Health Checkup 3d Printing Joints Tissue And Even Organs The Saturday Evening Post
3
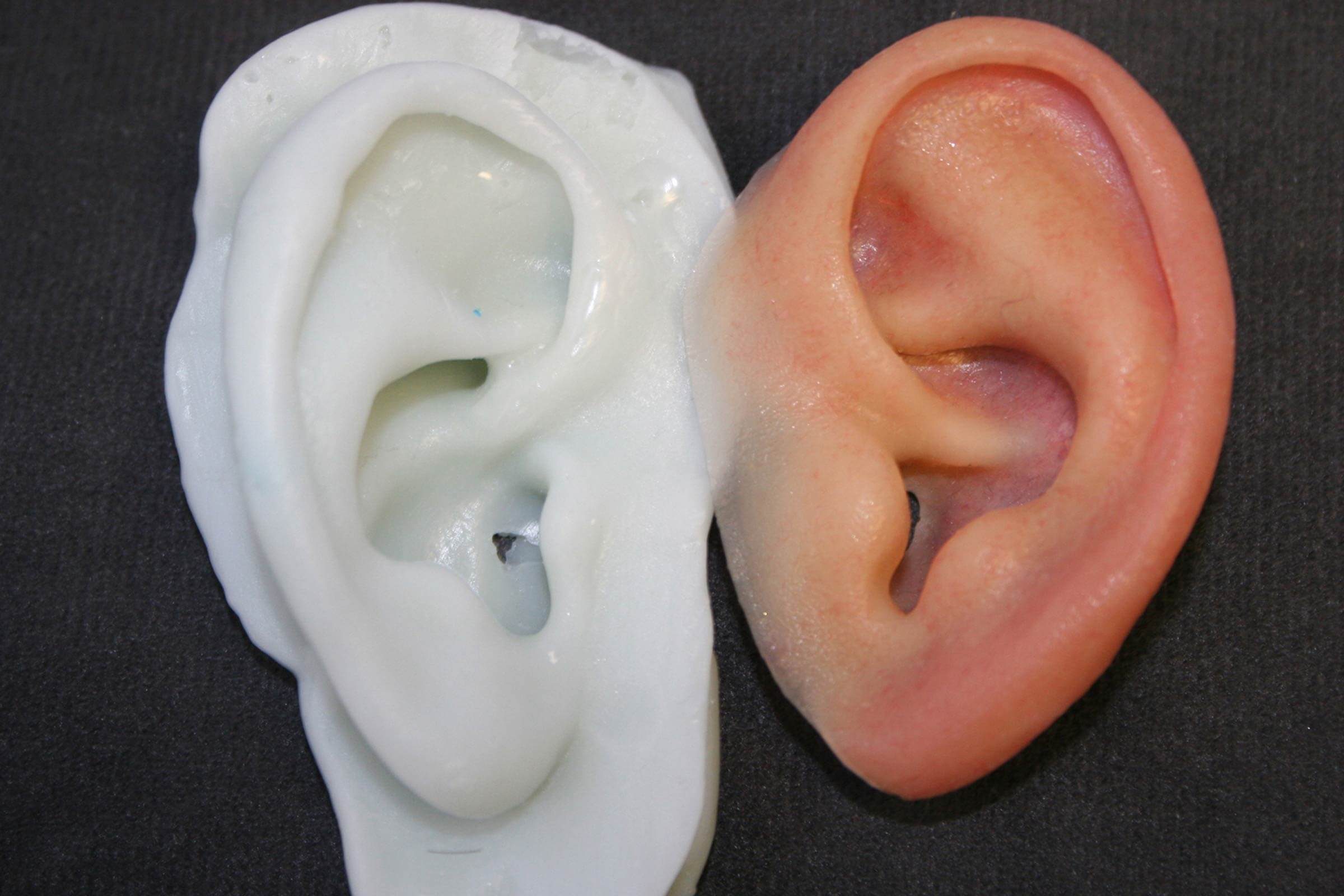
Here S How 3 D Printers Are Making Human Body Parts Reader S Digest
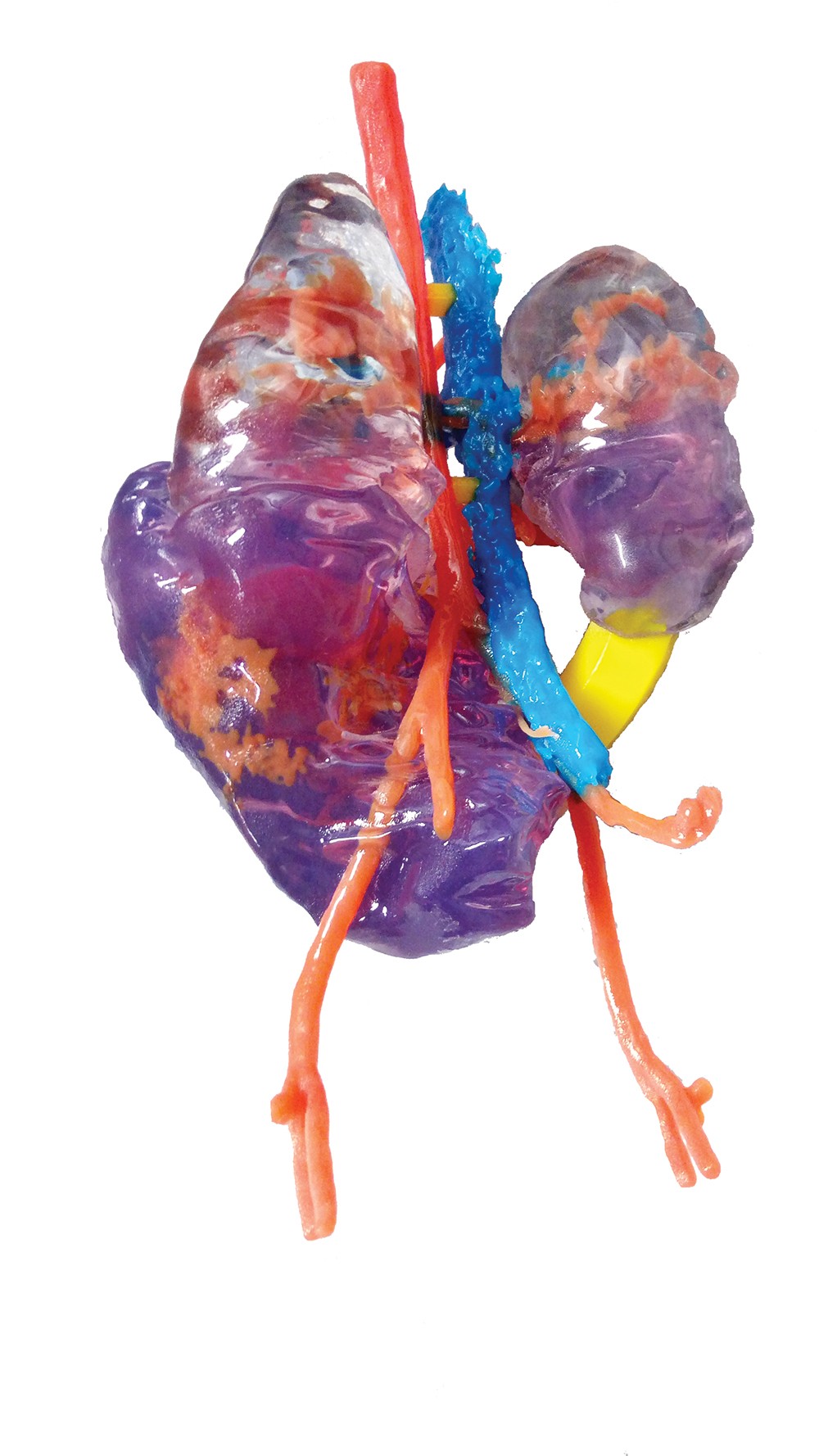
How Far Away Are We From 3d Printing Organs Medical Hudson Valley Chronogram Magazine

How Close Are 3d Printed Organs To Reality Medical Devices
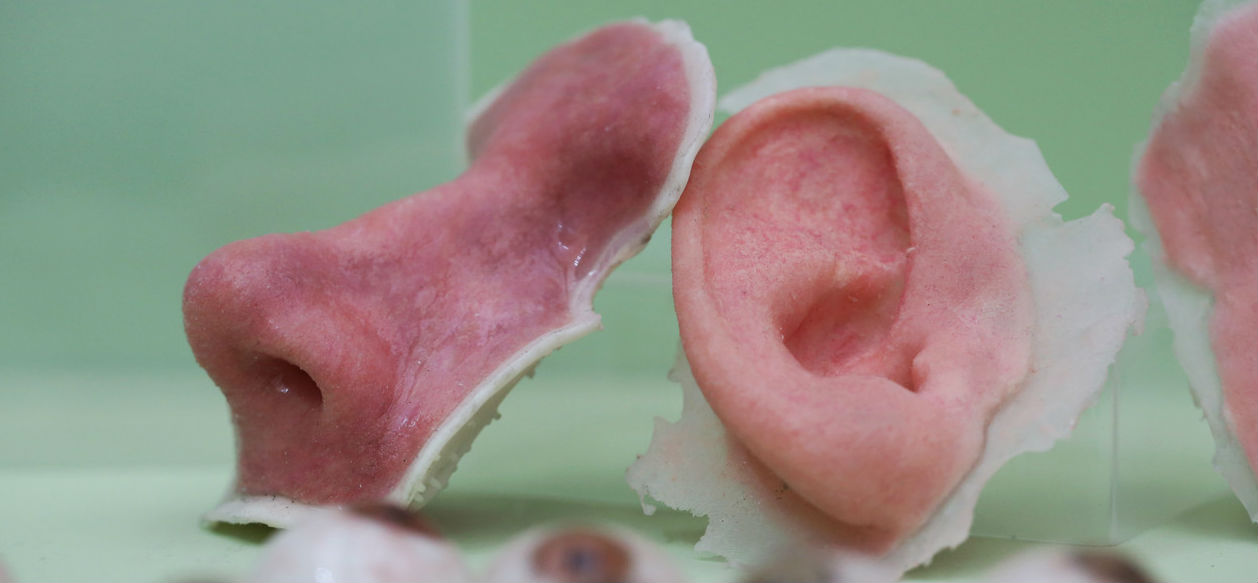

3d Printing Human Parts The Future Of Our Bodies Is 3d Printed Bioprinting World

3d Printing Technique Brings Hollywood To Human Organs Designnews Com

Mimicking The Growth Of Human Organs Through 3d Bio Printing Adam Feinberg Youtube

Stratasys Mimics Real Organs With 3d Printed Models Designnews Com

3d Printed Human Organs Test Chemical Drug Responses

Bio Inks Are The Key To Amazing New Medical Applications For 3d Printing Universal Sci

3d Printed Hearts With Beating Tissue Could Ease Organ Donor Shortage

3d Bioprinted Organ Models Key To 1 9 Billion Market 3d Printing Progress

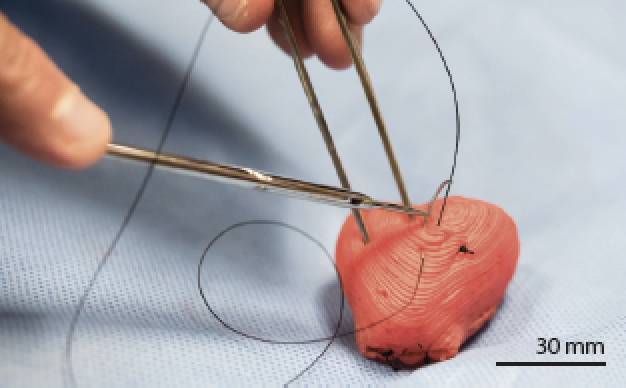
3d Bioprinting Creates Collagen To Rebuild Hearts Physics World
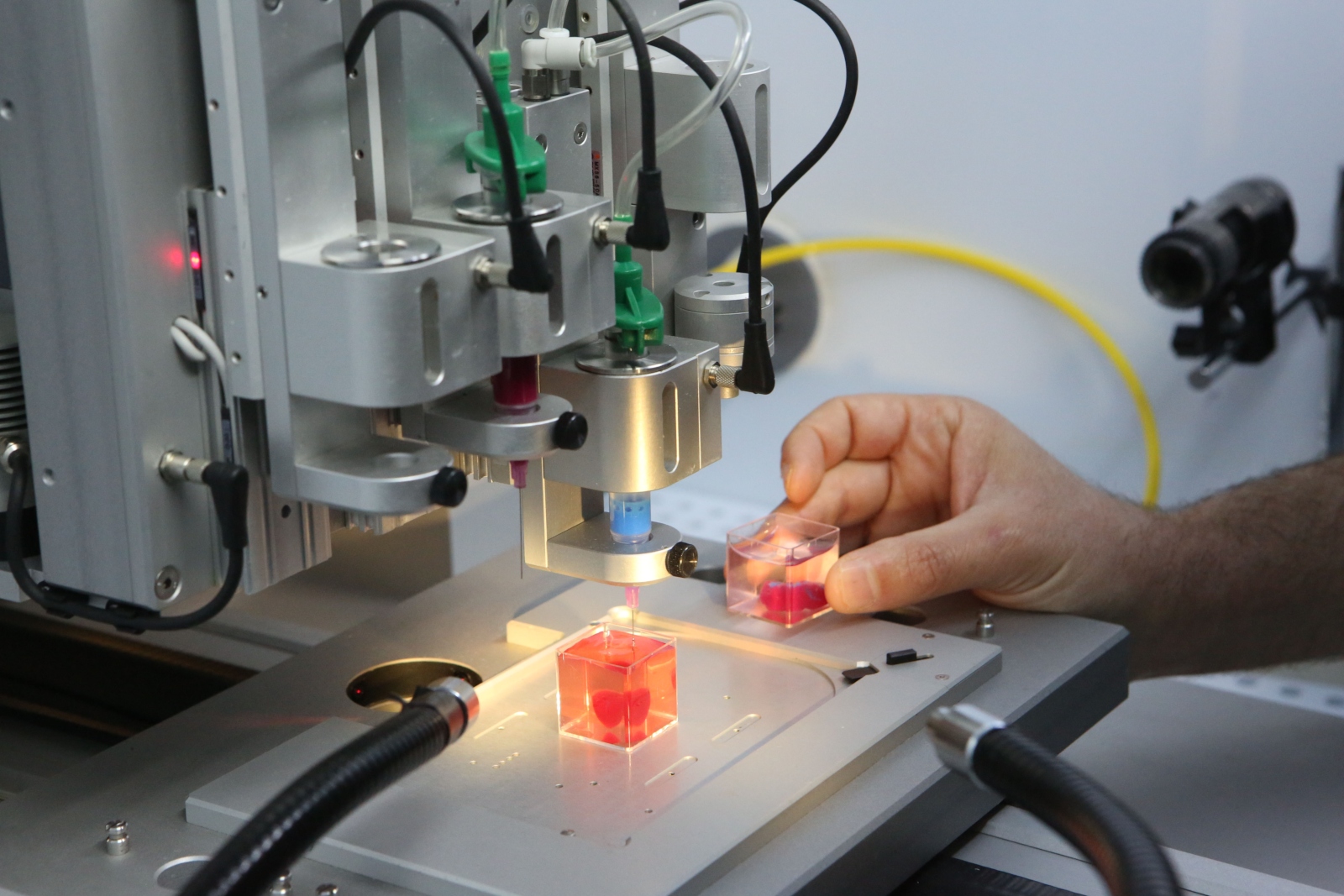
Israelis Create World S First 3d Printed Heart With Blood Vessels Israel21c
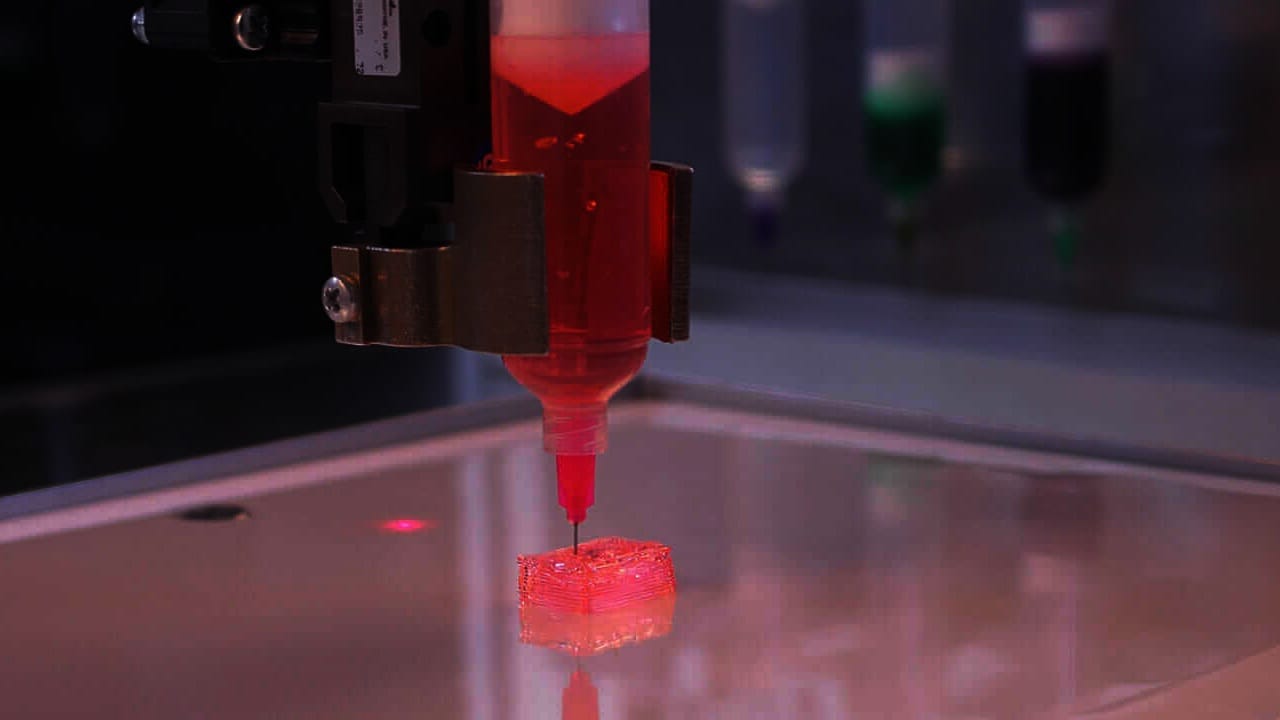
Space Station Cosmonaut Begins 3d Printing Study Of Living Tissue In Zero Gravity Technology News Firstpost

A Swifter Way Towards 3d Printed Organs Technology Networks

3d Printing Organs Moves A Few More Steps Closer To Commercialization Techcrunch

3d Printing Tissues And Organs Just Got Faster Machine Design

Breakthrough In The 3d Printing Of Human Organs Healthcare It Australia

3d Printed Organs And Body Parts Projects 3dnatives

Gel Scaffold Paves Way For 3d Printing Of Biological Organs New Scientist
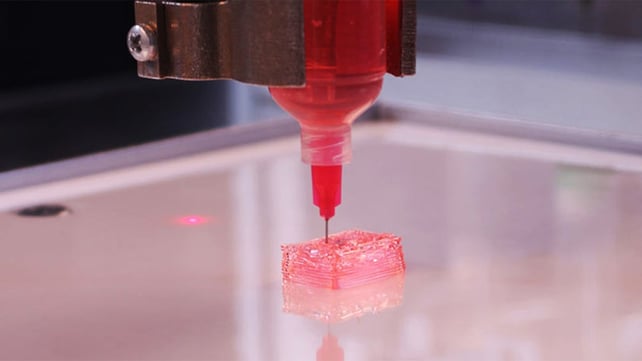
9utpzxwp6dmalm

3d Printed Tissues And Organs Without The Scaffolding 3d Printing Progress

Can 3d Printing Help The Organ Shortage Lifecenter

3d Printing And Tissue Engineering Science And Technology

How To 3d Print Human Tissue The Startup 3d Printing Human Organs To Save Lives Bioprinting World

This 3d Printer Creates Human Muscles And Tissues That Could Actually Replace Real Ones Quartz

On The Road To 3 D Printed Organs The Scientist Magazine

University Research Leads To Breakthroughs In 3d Printed Organs Ipwatchdog Com Patents Patent Law

Disruptive Technologies Beyond 30 For The Smart Planet Iii Ieee Future Directions
3
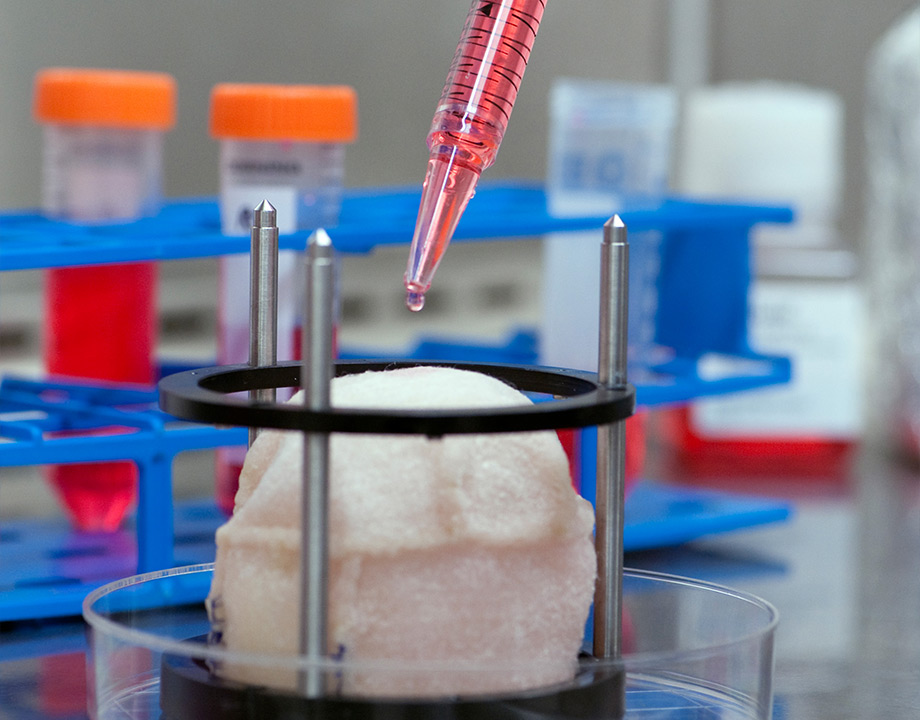
3d Printed Organs Nearing Clinical Trials Asme
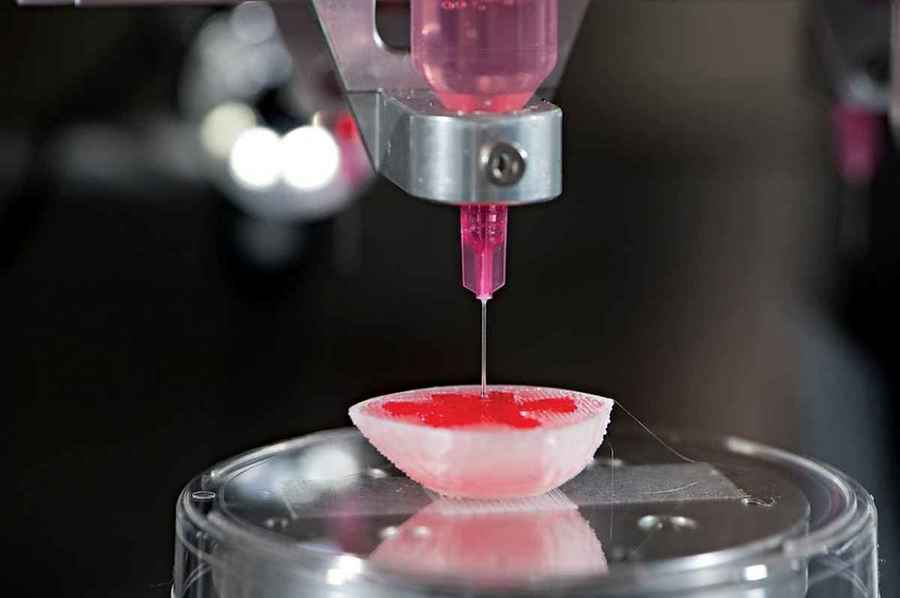

3d Printing Technique That Can Help Replicate Human Organs Developed Science News India Tv

How Medical 3d Printing Could Solve The Shortage Of Organ Donations Youtube

Researcher Believes 3d Printing May Lead To The Creation Of Superhuman Organs Providing Humans With New Abilities 3dprint Com The Voice Of 3d Printing Additive Manufacturing
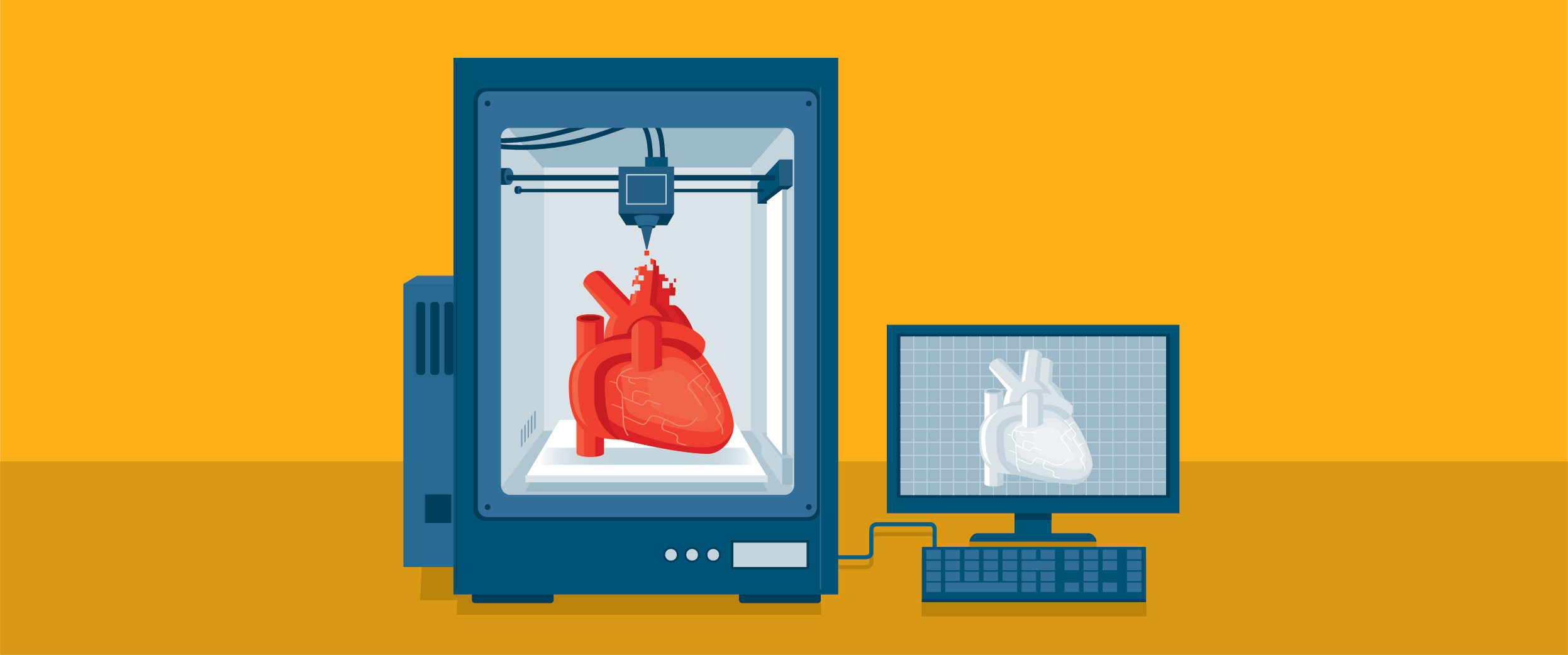
Using 3d Printing To Build Organs Implants And Medical Devices Labtag Blog
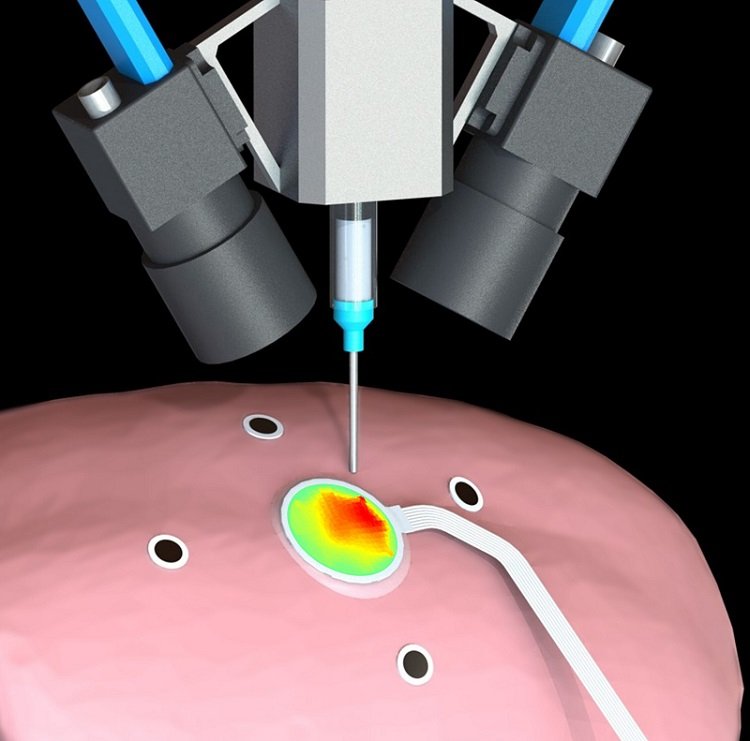
3d Printing Sensors On Expanding Organs Tectales ging Medical Technology
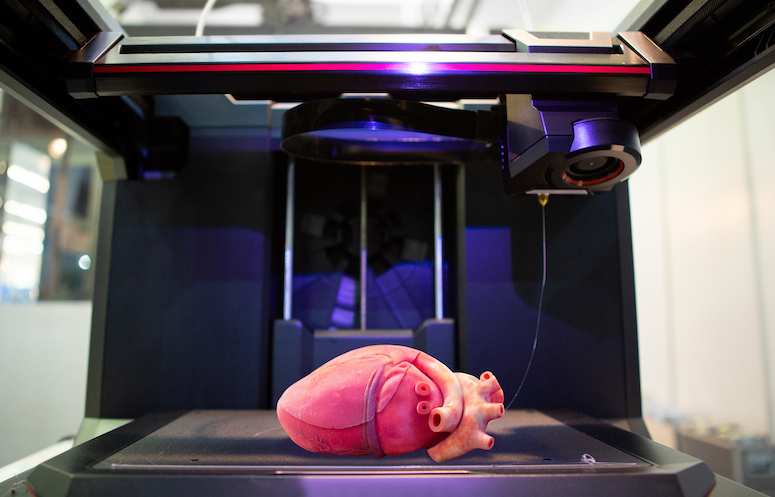

The Uncertainty Of Regulating 3d Organ Printing The Regulatory Review
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq76ltootjn9pqvk28ab5tmp X17rbq2zmvmoptsy2egvc8my7b Usqp Cau
The Next Frontier In 3 D Printing Human Organs Cnn

3d Printed Organs Set To Redefine Humanity Slideshow 3d Printing 3d Printing Technology 3d Printing Service

3d Bioprinting Is This The Future Of Organ Transplantation
Q Tbn 3aand9gctu6osbawmph1yvzoftm79p2tbsuxuju Gk2a Usqp Cau
Building Body Parts A Look Into The World Of 3d Printed Organs The Manitoban

How To Print Organs With A 3d Printer Illinois Science Council

How Soon Are 3d Printed Organs Coming Youtube

The Future Of 3d Printing Replication Of Human Organs 3d Printing Today 3d Printing News And 3d Printing Trends

Covid 19 New Discoveries Abound About The Mysterious Virus Fortune

3d Printing Technique Creates Super Soft Biological Structures

3d Printing Revolutionizing Medtech Pegus Digital

Affordable 3d Printed Organ Models For Medical Training Haptic

Researchers 3d Print Lifelike Artificial Organ Models

3d Printed Organs We Re Closer To Solving The Problem Of How To Supply Them With Blood 3d Printing Today 3d Printing News And 3d Printing Trends

The Printed Organs Coming To A Body Near You Nature News Comment
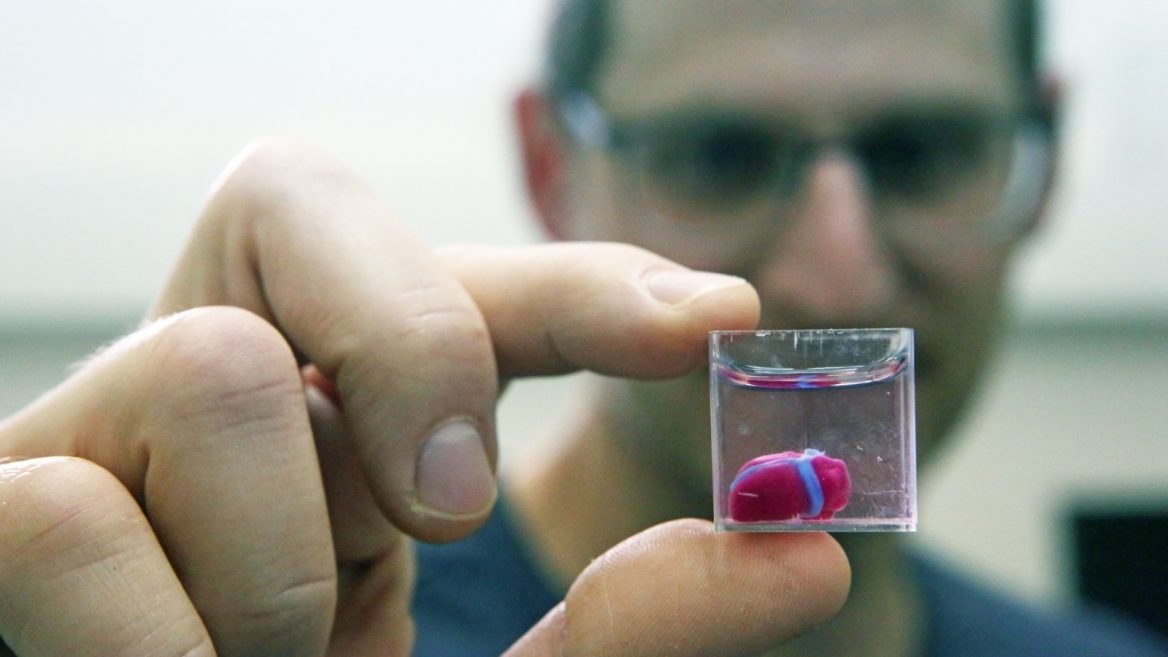

Israelis Create World S First 3d Printed Heart With Blood Vessels Israel21c
3d Printing Lifesaving Organs On Demand Breakthrough
Zero Gravity May Allow Viable Human Organs To Be 3d Printed Biospace

Applications Of 3d Printing Organs And Bio Printing
How A Pioneering 3d Printing Technique Is Revolutionising Healthcare The New Economy

The Emerging Industry Of 3d Printed Organs Will Become A Billion Dollar Industry Pioneering Minds
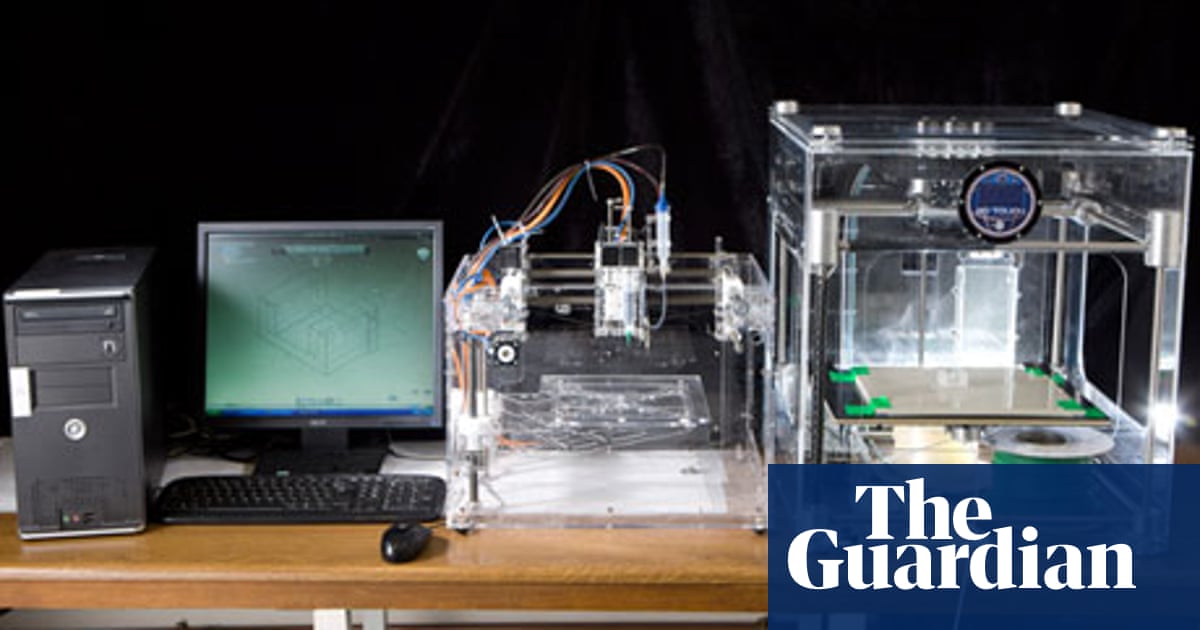

3d Printing Human Organs But Where S The Money For It Technology The Guardian
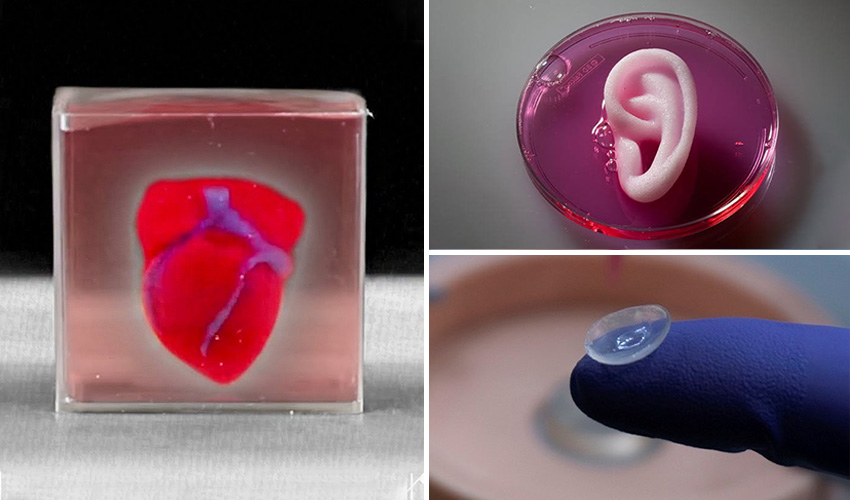
3d Printed Organs And Body Parts Projects 3dnatives
How Close Are 3d Printed Organs To Reality Verdict

3d Printed Body Organ Replacement Is It Really Safe For Humans 3d2go Philippines 3d Printing Services
3d Printed Kidneys Take Small Steps Toward Organ Replacements Live Science

Science News Organs Reproduced With 3d Printers For Surgeons Science News Express Co Uk
3d Printing Offers Hope Of Building Human Organs From Scratch Financial Times

Scientists Use 3d Printers To Make Miniature Organs For Testing Potential Covid 19 Drugs Science Times

How Scientists Are 3d Bio Printing Human Organs Youtube
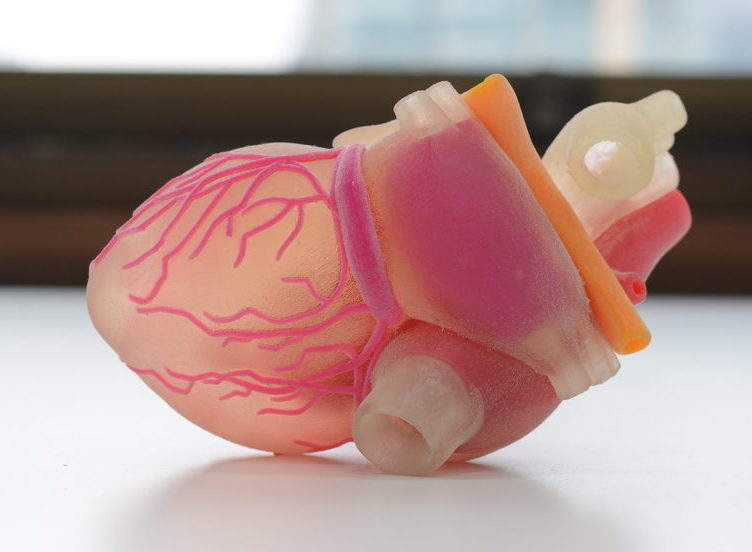
New Progress In The Biggest Challenge With 3d Printed Organs
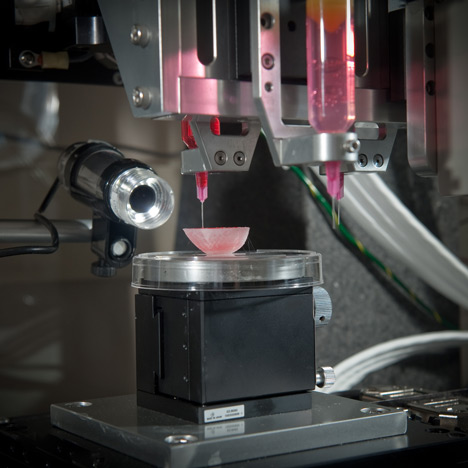
How 3d Printing Is Changing Health And Medicine
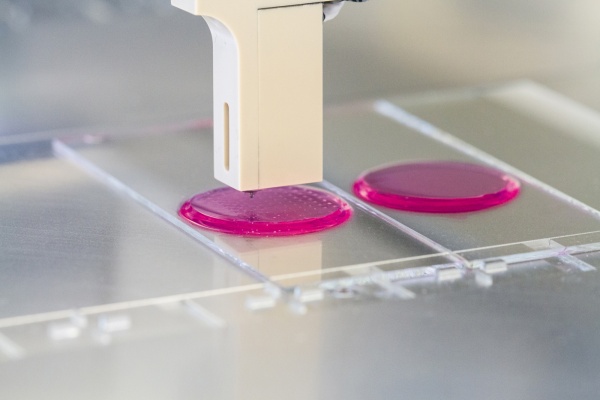

3d Printed Organs Usc Viterbi School Of Engineering

3d Printing Organs For Use In Surgical Planning Shows How Medical 3d Printing Is Changing Healthcare Biomedical 3d Printing Embodi3d Com

The Science Fiction World Of 3d Printed Organs
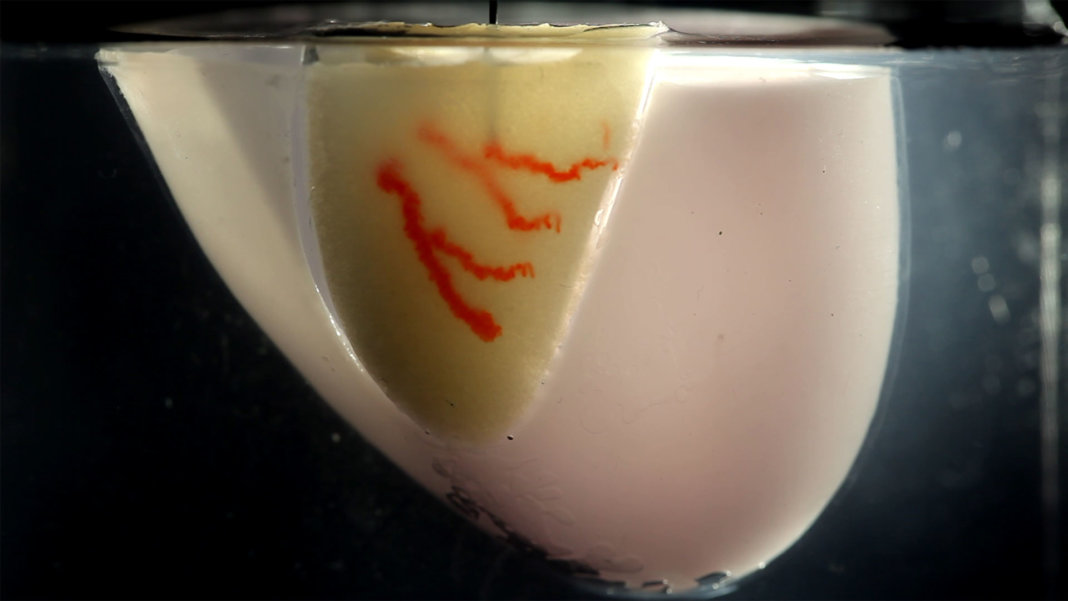
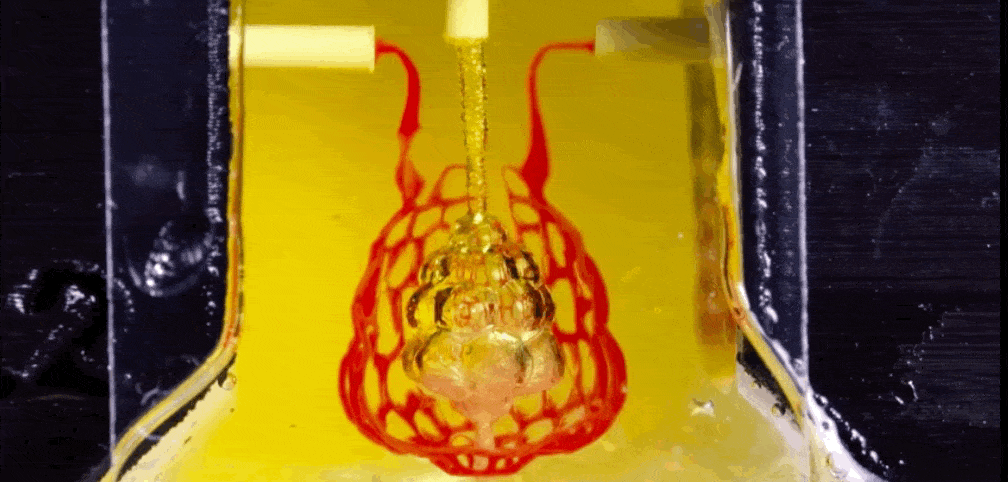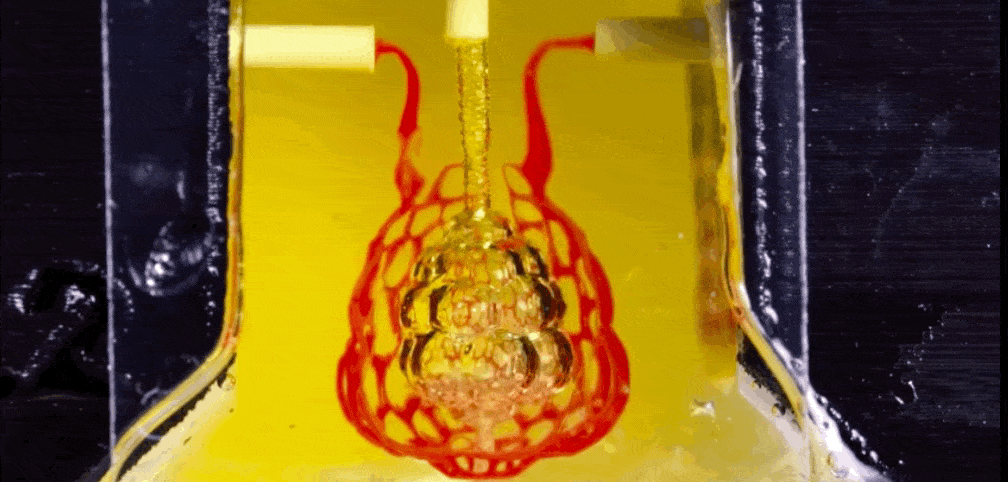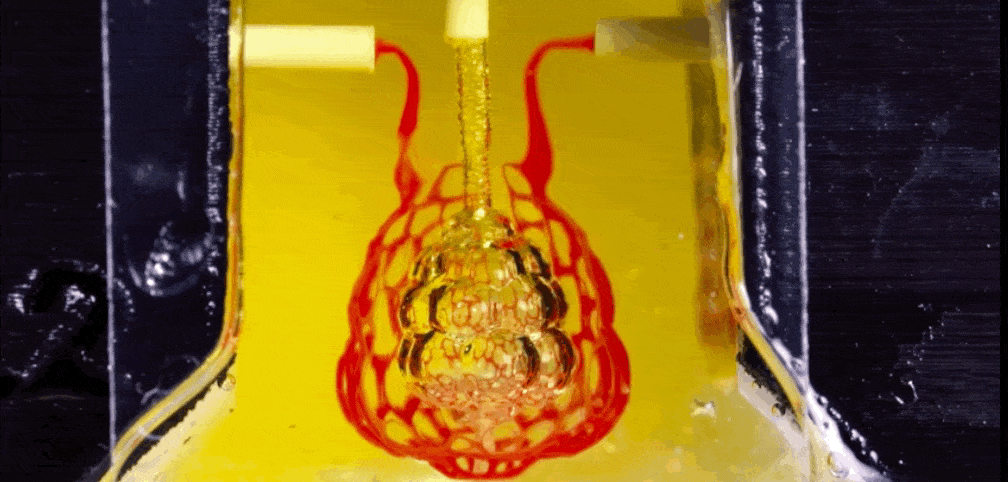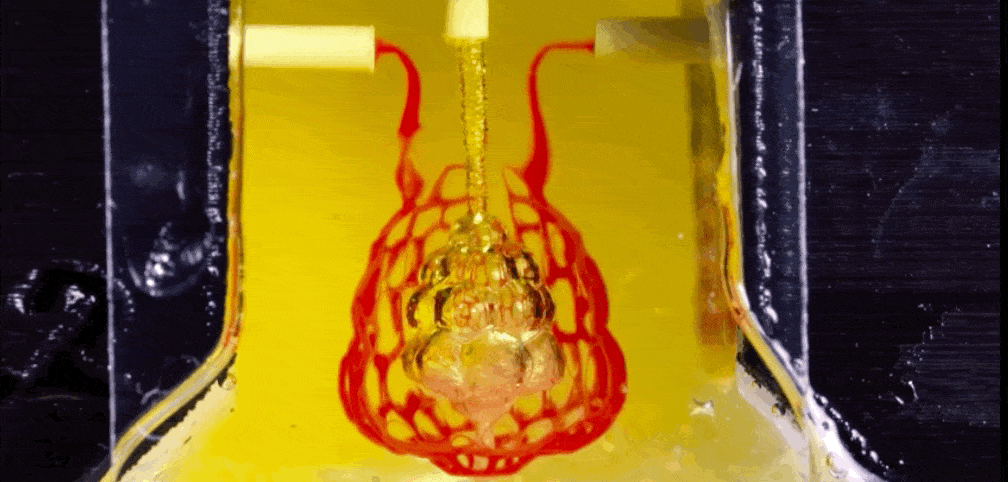
How A Centuries Old Sculpting Method Is Helping 3d Print Organs With Blood Vessels

Liquid In Liquid Printing Method Could Put 3d Printed Organs In Reach Science as

2d Stacking Method Could Make 3d Printed Organs Viable

The Science Fiction World Of 3d Printed Organs

3d Printing Revolutionizing Medtech Pegus Digital

Researchers 3d Print Lifelike Artificial Organ Models

3d Printed Human Organs Making Future Transplant Wait Lists Shorter

Why 3d Printing Organs Will Be Hard Difficulties Of Bioprinting 3d Printing Channel Videos 3d Printers Services Technology

3d Printing Organs Heading Toward Future Of Indestructible Humans

Israel S Collplant To 3d Print Human Organs
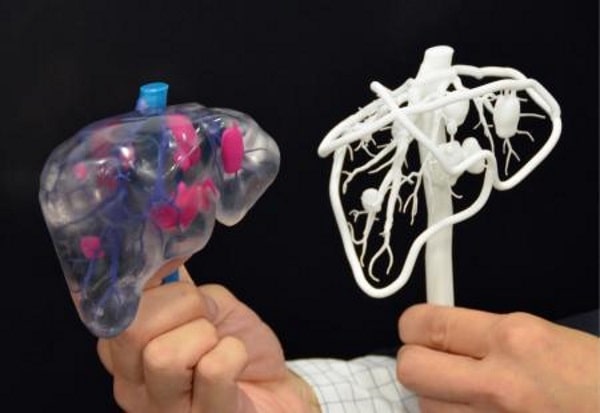
What Is The Future Of 3d Printed Organs Update
5 Most Promising 3d Printed Organs For Transplant All3dp

Here S How 3d Printers Are Making Human Body Parts Cellink China
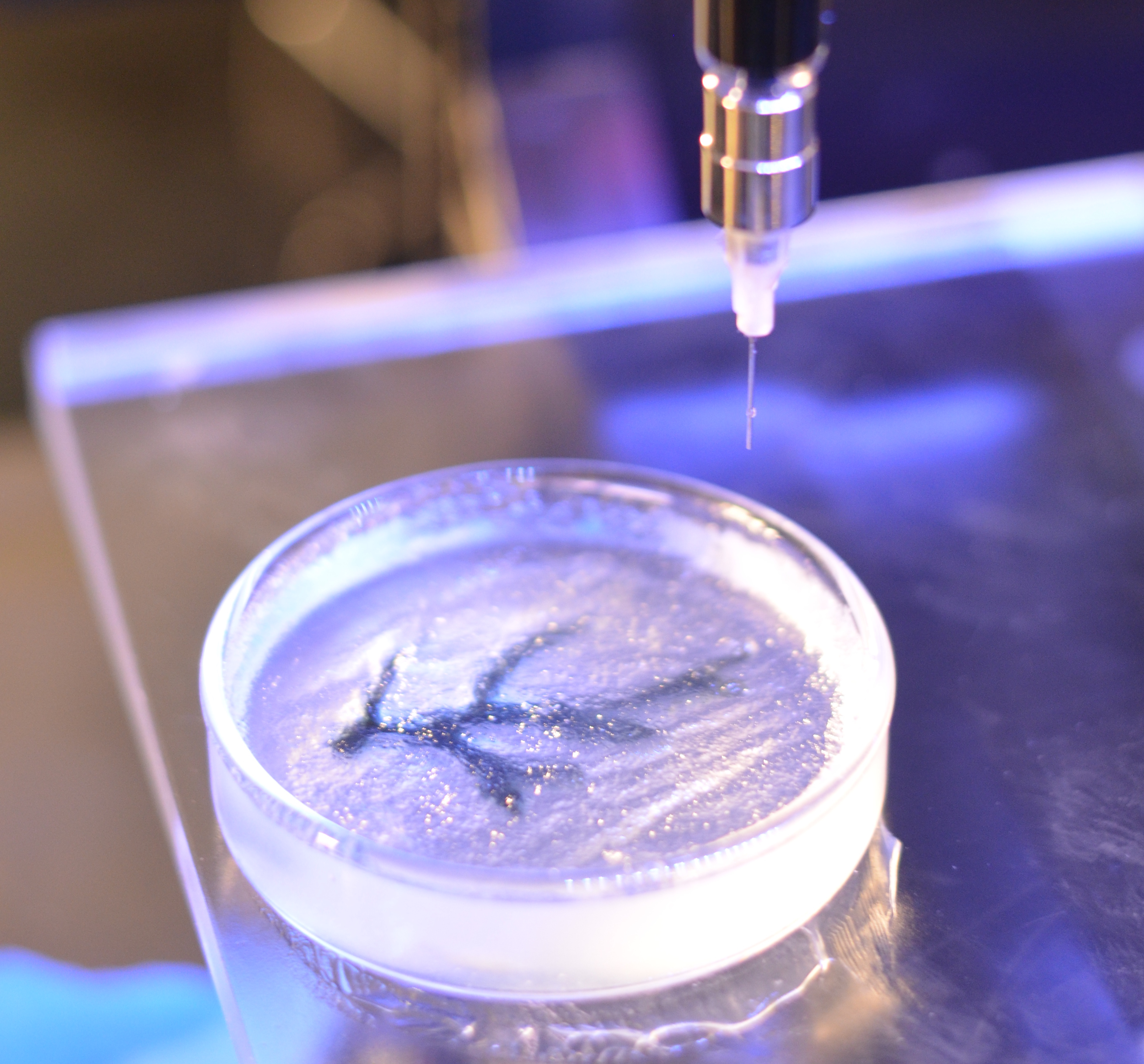

Building A Better Scaffold For 3d Bioprinting Nih Director S Blog

3d Printing Implants And Organs Is The New Reality Healthcare It Australia
3d Printed Miracles On Demand From Rx To Organs
Liver Success Holds Promise Of 3d Organ Printing Financial Times
3d Bioprinting Of Tissues And Organs Brings Life To Medical Science
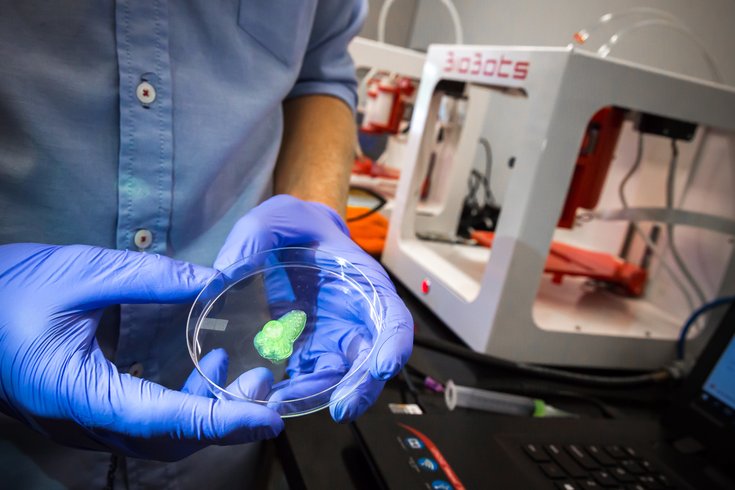

Philly S Biobots Develops 3d Printer To Make Human Tissue Phillyvoice

The Science Fiction World Of 3d Printed Organs

Exciting New Advances In 3d Printing Could Help Solve Cut Organ Transplant Waiting Lists
Scientists Can Now 3d Print Functional Organs Youtube



