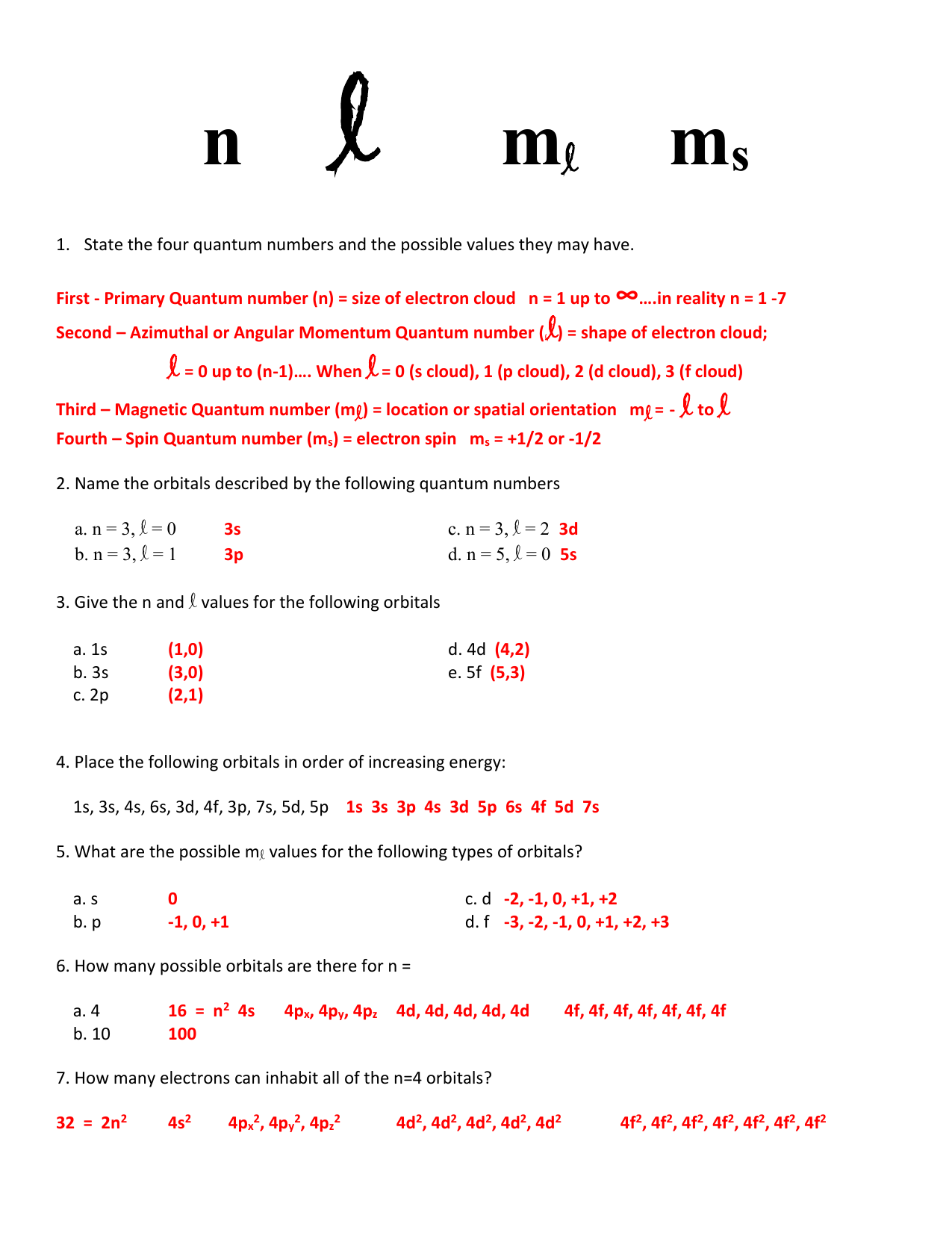
6s Orbital Quantum Numbers
Clarifying Electron Configurations Chemical Education Xchange
Answered 2 Use The Diagram N Dot Str The Vse 5 Bartleby

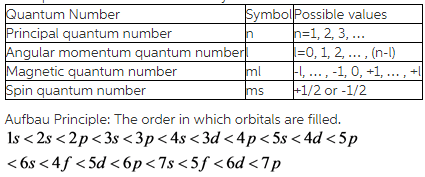
Quantum Numbers

Out Of 6s And 4f Orbitals Which Is Filled First And Why
Www Hudson K12 Oh Us Cms Lib08 Oh Centricity Domain 450 Quantum numbers ws Pdf
Light And The Modern Atom
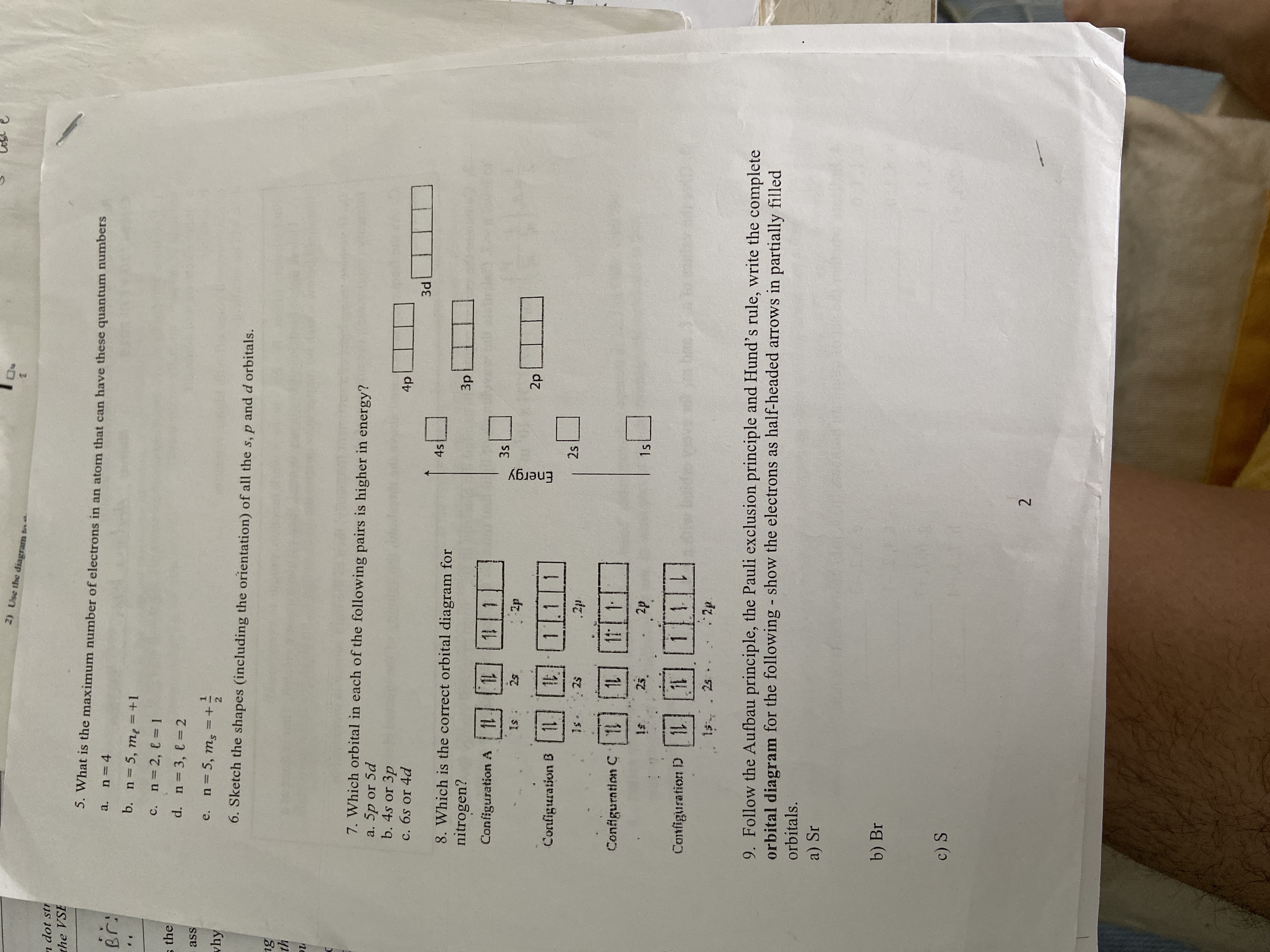
Quantum Numbers and Electron Configurations What is the electron configuration and orbital diagram for a phosphorus atom?.

6s orbital quantum numbers. The first, the principal quantum number, describes the overall size and energy of an orbital. What information is needed to determine the general shape of an orbital?. The magnetic quantum number tells to which orbital the electron belongs.
N is the principal quantum number. The quantum numbers n = 6 and l = 0 specify a 6s orbital. The angular momentum quantum number (l) is the type of orbital (s=0, p=1, etc).
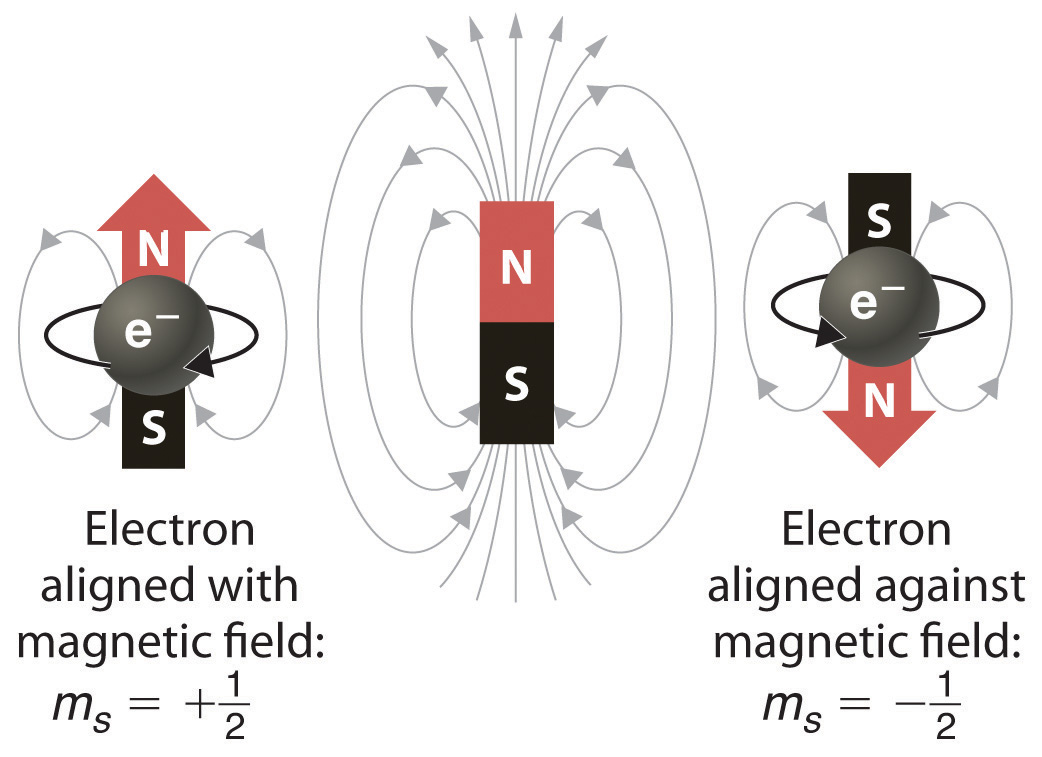
L = 0 specifies a spherical orbital. The fourth quantum number, m s , can have the value of +½ or –½. Each electron has its unique set of quantum numbers, which means that two electrons can share one, two, or even three quantum numbers, but never all four.
The quantum number ℓ must be less than n, which it is. What quantum numbers specify these subshells?. Because of the Pauli exclusion principle, there can only be two electrons per atomic orbital.
The principal quantum number (n) cannot be zero. The electron in an atom can be characterised by a set of four quantum numbers, namely principal quantum number (n), azimuthal quantum number (l), magnetic quantum number (m) and spin quantum number (s). This video explains s, p, d, and f orbitals, sublevels, and their shapes.
Which orbitals cannot exist?. According to quantum theory, the principal quantum number n specifies the size and energy level of the orbital. Which orbital is higher in energy:.
The relationship between three of the four quantum numbers to the orbital shape of simple electronic configuration atoms up through radium (Ra, atomic number ). Thus, a phosphorus atom contains 15 electrons. N = 3, l = 2.
The orbital letters are associated with the angular momentum quantum number, which is assigned an integer value from 0 to 3. In atomic theory and quantum mechanics, an atomic orbital is a mathematical function describing the location and wave-like behavior of an electron in an atom. Orbitals hold up to two electrons and because of the Pauli Exclusion principle a fourth quantum number is needed.
Identify the subshell in which electrons with the following quantum numbers are found:. The angular quantum number (l) can be any integer between 0 and n - 1. This atomic orbital describes a region of space in which there is a high.
We could write a pz orbital here, and then this one right here would be a py orbital. The orbitals that are usually the next highest in energy after the 6s orbitals are the:. Each electron in an atom is described by four different quantum numbers.
What Are Quantum Numbers?. Quantum numbers are a set of values that describes the state of an electron including its distance from the nucleus, the orientation and type of orbital where it is likely to be found, and its spin. It specifies the electron energy level (shell) and the total number of orbitals any given n value can have is n² so when n = 6 the maximum number of orbitals is.
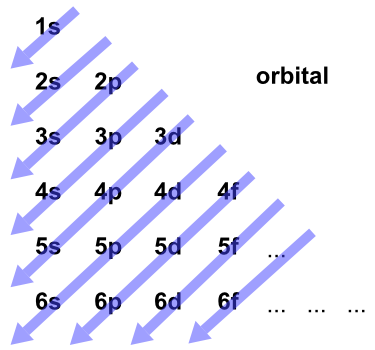
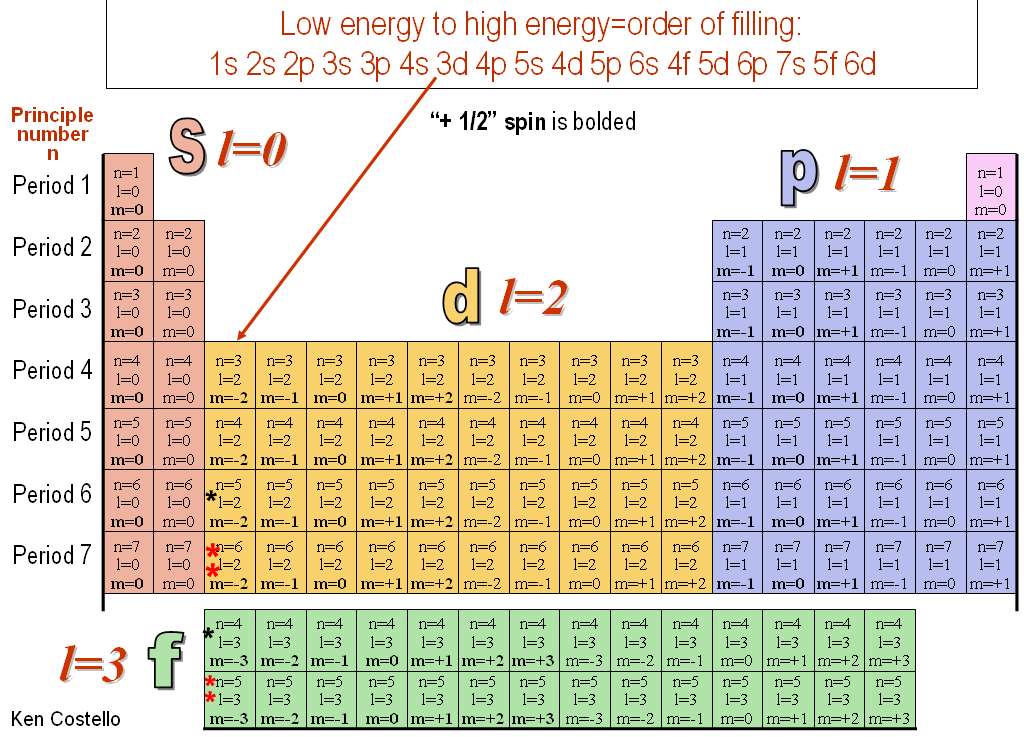
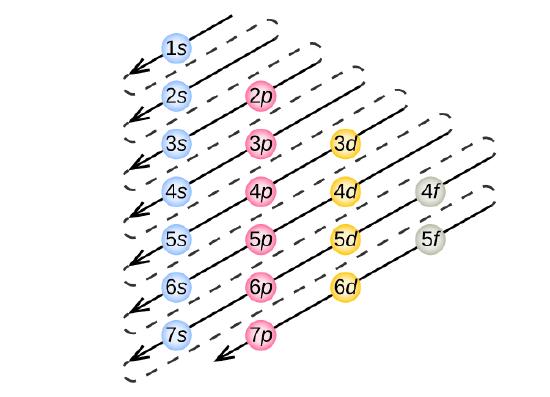
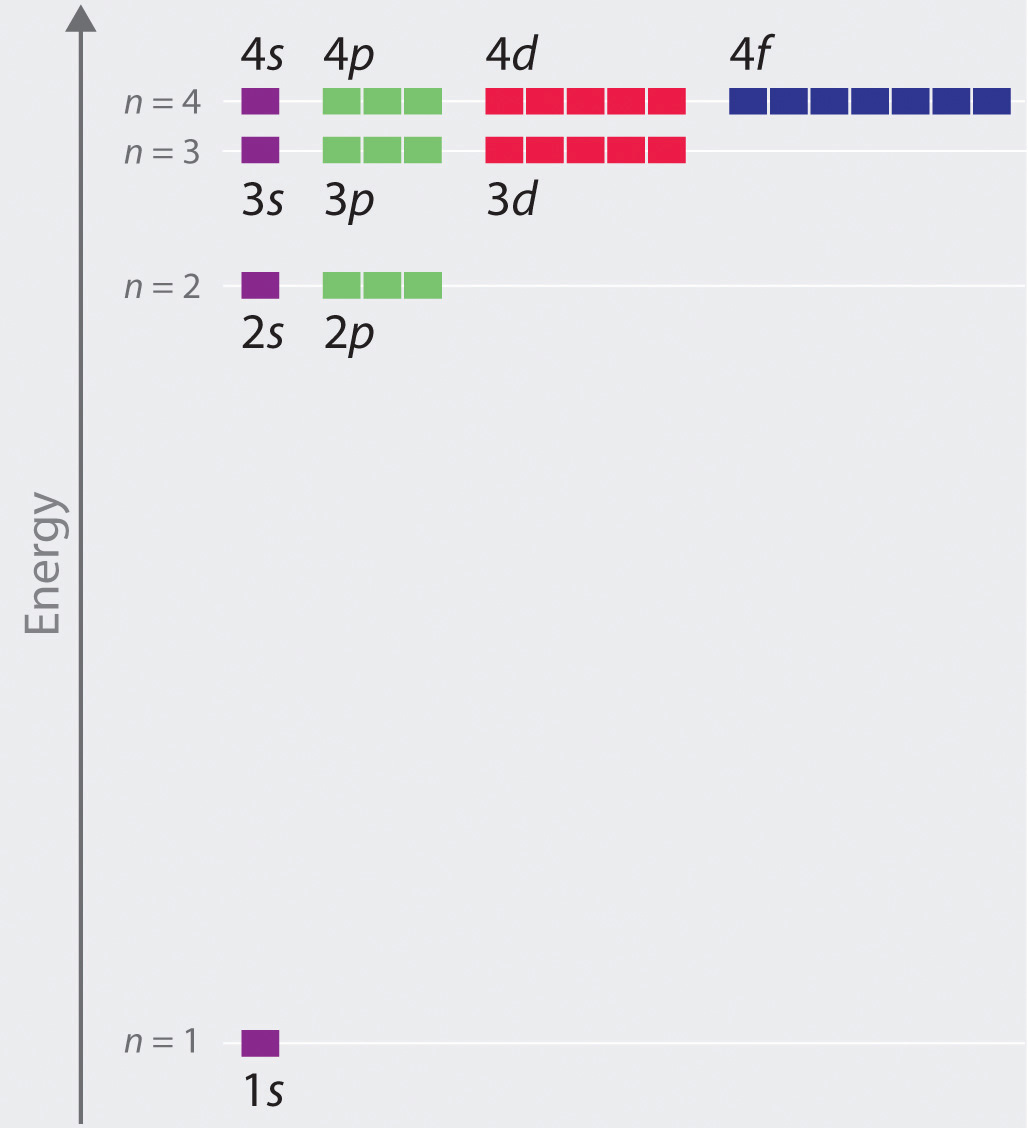
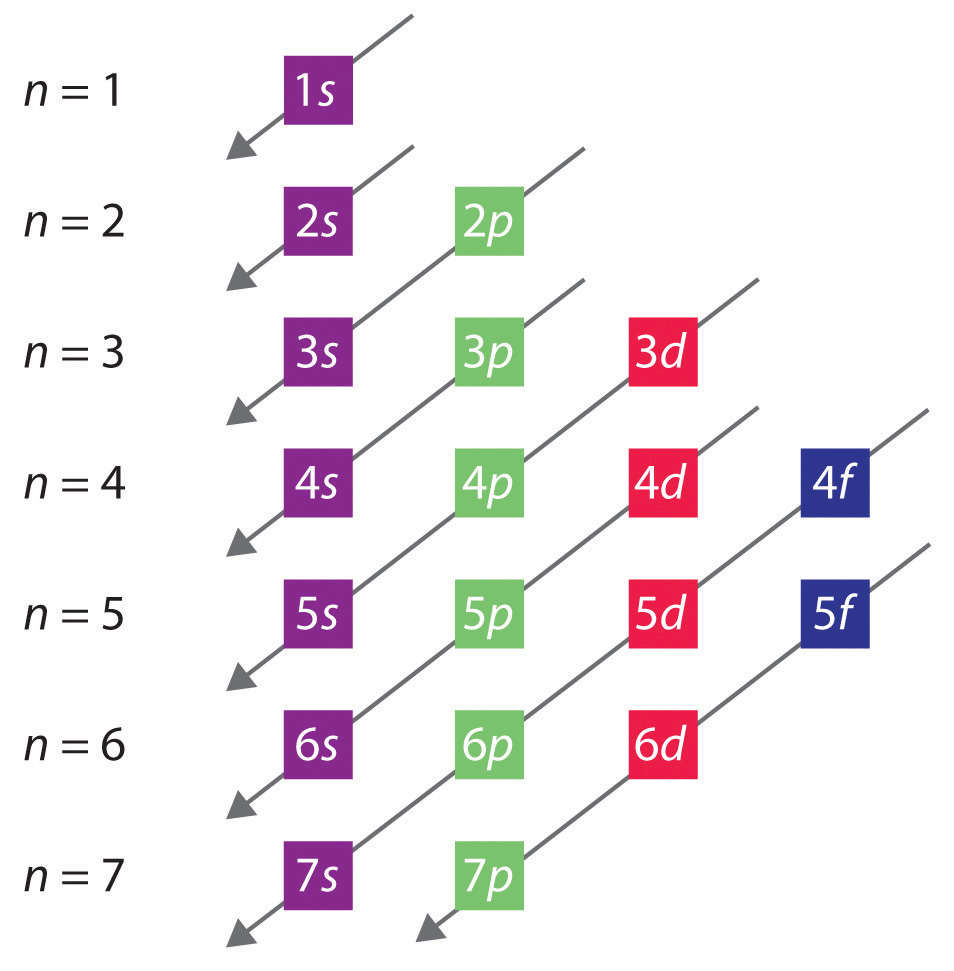
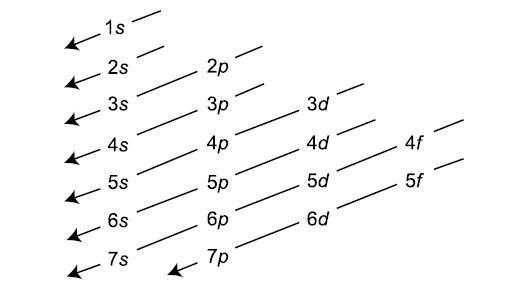
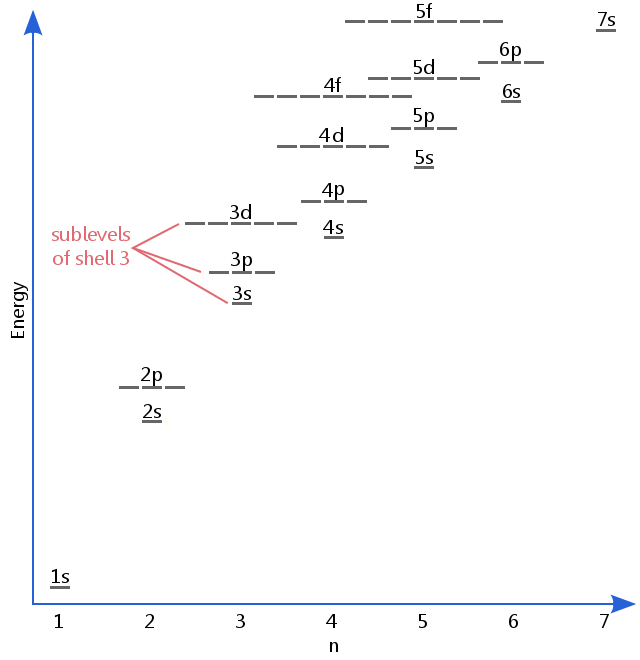
The order of filling of the energy levels is 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p. Principal Quantum Number (n):. Write a set of quantum numbers for a 4f orbital.
Table relating quantum numbers to orbital shape. The allowed values of n are therefore 1, 2, 3, 4, and so on. N=6, l=2 (s means l = 0 p means l = 1 d means l = 2 f means l = 3 g means l = 4 h means l = 5).
2p 3p 4d 3f 6s 2d 3f and 2d 5. The number before the orbital name (such as 2s, 3p, and so forth) stands for the principal quantum number, n. N = 1, 2, 3, …, ∞.
This section covers some of the more important quantum numbers and rules—all of which apply in chemistry, material science, and far beyond the realm of atomic physics. The second quantum number is the angular quantum number, ℓ. 0, 1, 2, 3, and so on.
The spin quantum number. For s orbitals, =0. Quantum Numbers and Atomic Orbitals.
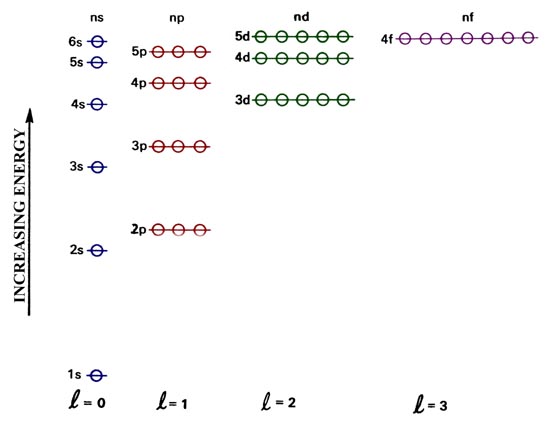
Theoretically, n can go up to infinity, but physicists have not yet created any atoms that require a principal quantum number bigger than 7. Don't worry, nobody understands these in first-year chemistry. Within multi-electron atoms, the fact that the 2s orbital is lower in energy than the 2p orbitals is called a “loss of degeneracy within energy levels.
The s correlates to 0, p to 1, d to 2, and f to 3. Spin Quantum Number (ms):. For the elements in the periodic table, n = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7.
Second Quantum Number. Basically, it defines the shape of an orbital. How Do 2p Orbitals Differ From.
M l, the magnetic quantum number defines the spatial orientation (direction) of an orbital. N = 4 l = 3 ml = 3, 2, 1, 0, -1. Quantum numbers may be defined as a set of four numbers with the help of which we can get complete information about all the electrons in an atom.
The second, the angular momentum quantum number (AMQN), determines the specific characteristic shape of an orbital. Doi:10.1016/ 0022-1902(61)-5 Allred, A. Each s orbital also has a number associated with it, called the principal quantum number, and abbreviated n.
N represents the energy level,. The angular Momentum Quantum Number (l) indicated the shape of the orbitals. The spin quantum number is +1/2, which is allowed.
This function can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron of an atom in any specific region around the atom's nucleus.The term atomic orbital may also refer to the physical region or space where the electron can be. Revise Your Analogy If Necessary. The number corresponds to the quantum number n, and the letter corresponds to the quantum number.
As the principal quantum number increases, the orbital becomes larger and will have a higher energy level. In other words, no two electrons in an atom or molecule can have the exact same set of quantum numbers. It tells us the address of the electron i.e., location, energy, the type of orbital occupied and orientation of that orbital.
The size of the s orbital is also found to increase with the increase in the value of the principal quantum number (n), thus, 4s > 3s> 2s > 1s. Specifies the orientation of the spin axis of an electron. So the notation looks like this, "nl#".
Because n describes the most probable distance of the electrons from the nucleus, the larger the number n is, the farther the electron is from the nucleus, the larger the size of the orbital, and the larger the atom is.n can be any positive integer starting at 1, as \(n=1. M s = +½ or -½. An electron can spin in only one of two directions (sometimes called up and down).
The allowed quantum numbers for the H atom are given in the tables below. We're going to have the n quantum number followed by the letter that represents the l sublevel. Define a unique orbital) 4.
Suggest An Analogy Not Mentioned In This Section To Help Explain The Four Quantum Numbers. We have three orbitals, we have three p orbitals here, one for each axis. Feedback The names 1 s, 2 s, 2 p, 3 s, 3 p, etc.
For a given value of l, there are (2l +1) values of m. A wave function for an electron in an atom is called an atomic orbital;. It is defined as the three dimensional space where probability of finding electrons are maximum.
Each p orbital consists of two sections better known as lobes which lie on either side of the plane passing through the nucleus. There is nothing wrong with the following set of quantum numbers:. The secondary quantum number l specifies the shape of the orbital.
And the quantum number l which tells us about the shape of that orbital. Quantum Number Allowed Values Name and Meaning n n = 1, 2, 3,. List all the possible quantum numbers for an electron in the (a) 2s orbital (b) 6s orbital (c) 5f orbital Get more help from Chegg Get 1:1 help now from expert Chemistry tutors.
What are the four quantum numbers for the last electron added?. Let's go to the last quantum number. The letter in the orbital name defines the subshell with a specific angular momentum quantum number l = 0 for s orbitals, 1 for p orbitals, 2 for d orbitals.
What is the total number of electrons possible in the 6s orbital?. N is the principal quantum number. I) Principal quantum number(n):.
This number is also known as the orientation quantum number because it gives the distribution of electron clouds in space around the nucleus. References (Click the next to a value above to see complete citation information for that entry). You just pretend to, and then in second-year you learn them.
For d orbitals, =2. The fourth quantum number, the spin, is a property of individual electrons within a particular orbital. "Electronegativity Values from Thermochemical Data." Journal of Inorganic and Nuclear Chemistry, volume 17, number 3-4, 1961, pp.
The spin quantum number is m sub s here. The angular momentum quantum number can be used to give the shapes of the electronic orbitals. N = 4 l = 1 3 (the 4p orbitals) n = 2 l = 2 none (l must be < n) n = 3 l = 2 5 (the 3d orbitals) n = 5 l = 1 ml = -1 1 (3 q.n.
A total of 10 sets of quantum numbers can be used here. The principal quantum number is related to the size and energy of the orbital. This limits the number of electrons allowed per subshell.
1 and 1s2 are allowed, but 1s3 is not. An electron configuration for an atom is simple a list of the occupied sub-levels showing the number of electrons in each sub-level. Best we can do!.
When Schrödinger equation is solved for a wave function Ψ, the solution contains the first three quantum numbers n, l and m. The last quantum number is the spin quantum number. For an electron in the 6s orbital, the quantum numbers n and are 6 and 0, respectively.
The principal quantum number n must be an integer, which it is here. S orbitals are spherical, centered on the nucleus. L 2 = ħ 2 ℓ (ℓ + 1) In chemistry and spectroscopy, ℓ = 0 is called an s orbital, ℓ = 1 a p orbital, ℓ = 2 a d orbital, and ℓ = 3 an.
The third, the magnetic quantum number, denotes. Each value of n has multiple values of ℓ ranging in values from 0 to (n-1).This quantum number determines the 'shape' of the electron cloud.In chemistry, there are names for each value of ℓ. This would be a pz orbital.
It discusses the 4 quantum numbers n, l, ml, and ms. There are 4 types of orbital:. For p orbitals, =1.
By solving the Schrödinger equation (Hy = Ey), we obtain a set of mathematical equations, called wave functions (y), which describe the probability of finding electrons at certain energy levels within an atom. The Shape of p Orbitals. For each principal quantum number n (sometimes called the shell) there is just one s-orbital (eg 1s, 2s, 3s etc) and for principal quantum numbers 2 and above three p orbitals.,(2px, 2py, 2pz, 3px.
The allowed values of l are 0, 1, 2, 3 … n - 1. For a 6s orbital, n = 6. The Principal Quantum Number (\(n\)) The principal quantum number, \(n\), designates the principal electron shell.
Create A Chart Showing The Information You Can Obtain From The Quantum Numbers N, I, And M, 2. The same quantum state. For an electron in the n = 3 shell that have an angular momentum quantum number l = 1 and a spin quantum number m_s = 1/2.
The first three (n, l, m l) specify the particular orbital of interest, and the fourth (m s) specifies how many electrons can occupy that orbital. Are known as spectroscopic notations. Share It With A Classmate And Get His Or Her Feedback.
The three quantum numbers (n, l, and m) that describe an orbital are integers:. What is the maximum number of orbitals with:. Which quantum number does NOT give information about an individual orbital?.
Orbitals & Quantum Numbers:. Another change is that while the quantum number n still plays the prominent role, it is augmented by the quantum numbers l, m l, and m s. The first value, ℓ = 0 called an s orbital.
L is the angular momentum (or "azimuthal") quantum number;. This quantum number gives the possible orientation of the orbital in the space. These four numbers, n, ℓ, m, and s can be used to describe an electron in a stable atom.
F orbitals-- There are _____ ways to place f orbitals on the 3 axes in space, that’s why there are ____ orbitals per energy level. As you know, we use four quantum numbers to describe the position and spin of an electron in an atom. Because this set of quantum numbers follows all restrictions, it is possible.
The values of quantized entities are expressed in terms of quantum numbers, and the rules governing them are of the utmost importance in determining what nature is and does. What are the four quantum numbers and what does each specify?. Okay, there are four quantum number, three of which give the specifications an orbital.
It defines the energy and size of an orbital. S - orbital (maximum. According to the Bohr Bory principle E= n+l Where E is the energy of the orbitals,n is the principal quantum number and l is the azimuthal quantum number Now according to the Aufbau's principle electrons are filled in the orbitals with their incre.
The m ℓ quantum number must be between −ℓ and ℓ, which it is. The Pauli exclusion principle (Wolfgang Pauli, Nobel Prize 1945) states thatno two electrons in the same atom can have identical values for all four of their quantum numbers. Atom Orbital Neff a) Orbital ~‘~‘eff He is O.8~6 Be 2s 1.30 B 2s 1.22 2p 1.50 C 2s 1.18 2p 1.43 N 2s 1.14 2p 1.38 O 2s 1.12 2p 1.34 F 2s 1.11 2p 1.32 Si • ~ 3s 1.51 3p 1.56 S 3s 1.42 3p 1.46 Ci 3s 1.38 3p 1.43 Ge 4s 1.73 4p 1.77 Se 4s 1.67 4p 1.69 Br 4s L64 4p 1.65 Sn 5s 1,86 3p 1.92 Te 5s i.~i Sp L.~-4~ I Ss 1.79 5p 1.81 Pb 6s 1.98 6p 2.04 P0 6s 1.94 6p 1.97 Ni 3d 1.49 4s 1.80 Pt Sd 1.
Write all the possible sets of magnetic quantum numbers, m_l. Solution The atomic number of phosphorus is 15.

Solved Apply The Pauli Exclusion Principle A Indicate W Chegg Com

Clarifying Electron Configurations Chemical Education Xchange
How To Answer Which Orbitals Are Possible For Ex 1p 2s 2p 3f Which Of The Following Are Possible Orbitals And Why Quora

Electronic Structure Of Atoms Electron Configurations Chemistry Openstax Cnx
Atomic Clocks
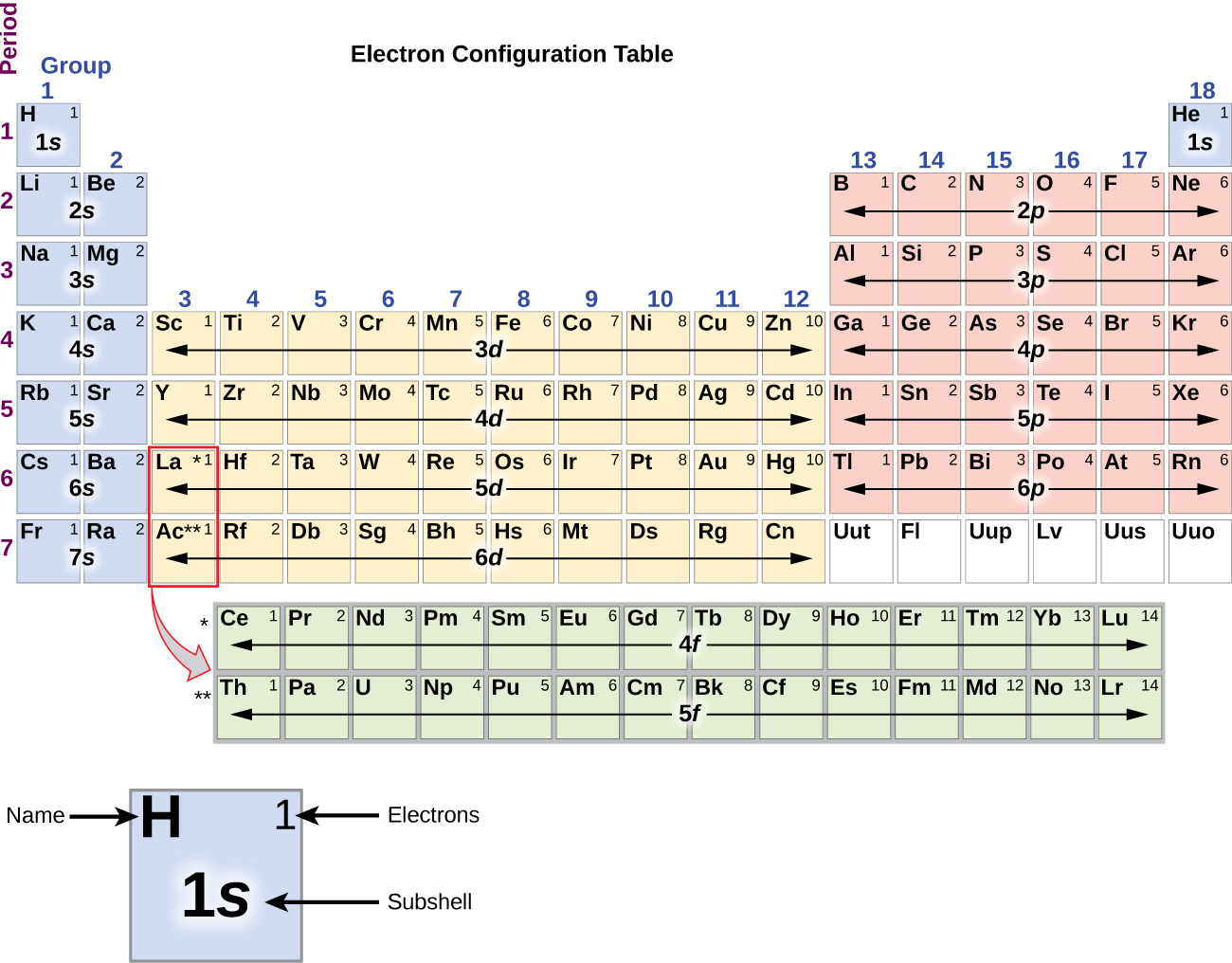
8 3 Electron Configurations How Electrons Occupy Orbitals Chemistry Libretexts

Unit 2 Quantum Numbers Review Packet

Solved 13 Consider 3px And 3py Orbitals Which Quantum N Chegg Com

Periodic Table The Basis Of The Periodic System Britannica
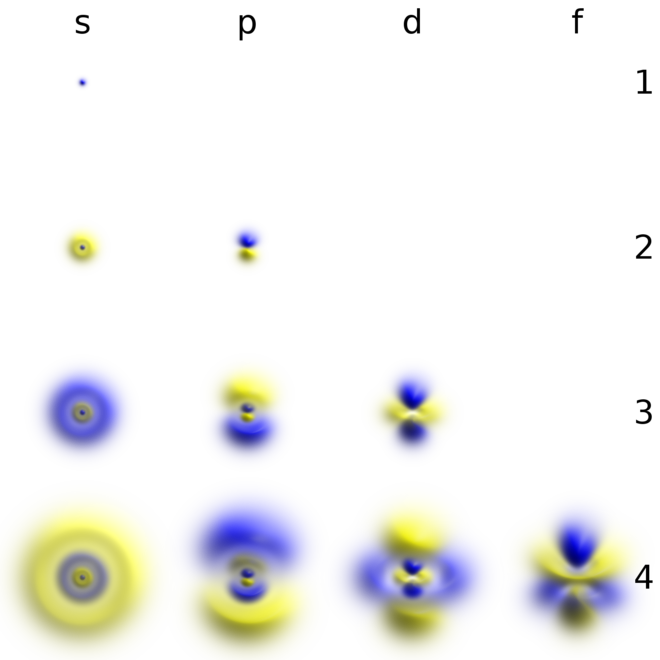
Atomic Orbital Wikiwand

Quantum Numbers Worksheet

Di Tuujmcuous Use Of The Same When Electrons Are Added In The 6s Orbital What Happens To The Energy Level Of The 5d Orbitals As A Result After The Electron Enters 5d
Http Skeatingscience Weebly Com Uploads 8 8 0 2 Quantum Worksheet Pdf
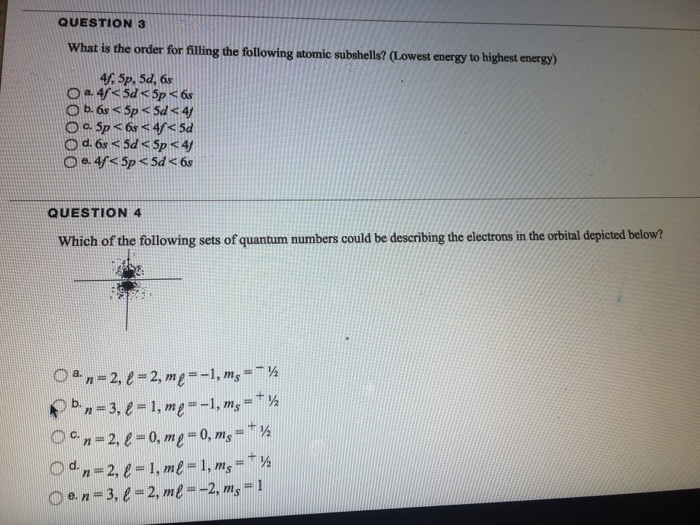
Solved What Is The Order For Filling The Following Atomic Chegg Com

Quantum Numbers And Atomic Orbitals Angelo State Pages 1 4 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5
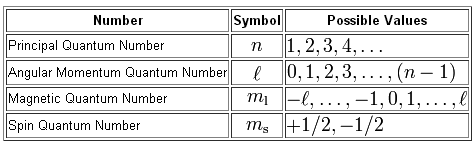
How To Assign 4 Quantum Numbers To 2 Electrons In 3p Orbitals Socratic

Aufbau Principle Wikipedia

The Relativistic Contraction Of The 6s Orbital And Expansion Of The 5d Download Scientific Diagram

What Is The Total Number Of Electrons Possible In The 6s Orbital
6 4 Electronic Structure Of Atoms Electron Configurations Chemistry Libretexts
Many Electron Atoms The Electronic Basis Of The Periodic Table
Www Philadelphia Edu Jo Academics Ajaber Uploads Ch 6 Quantum theory and the electronicstructure of atom Part3 Pdf

Quantum Number Wikipedia

Principal Quantum Number An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Chemistry Practice Paper Electron Configuration Electron

Quantum Numbers Atomic Orbitals And Electron Configurations
The Lanthanides

What Is The Maximum Number Of Electrons That Can Occupy The L 4 Subshell What Are The Possible Sets Of 4 Quantum Numbers For An Electron In N 4 Orbitals Socratic
The Lanthanides
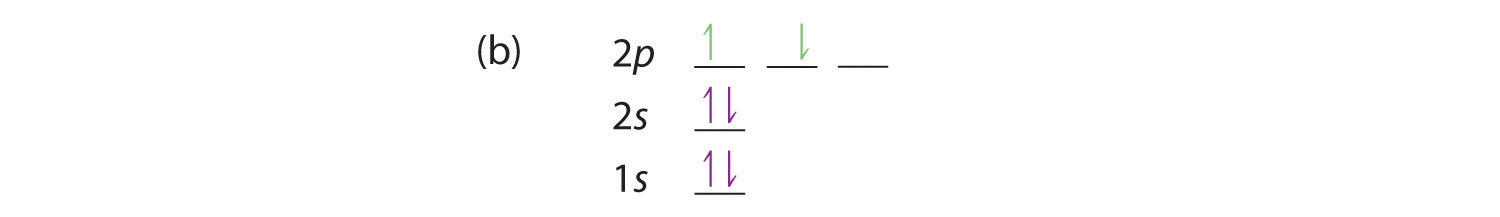
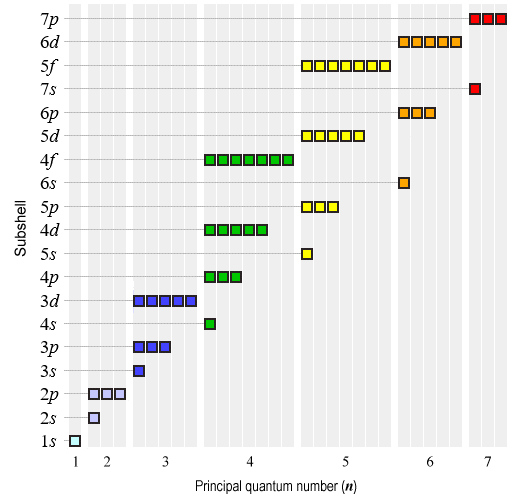
Building Up The Periodic Table

Oneclass How Many Orbitals Does The 6s Subshell Have A 0 B 1 C 2 D 3 E It Varies What Is The Va

What Is The Total Number Of Electrons Possible In The 6s Orbital
3 4 Electronic Structure Of Atoms Electron Configurations Chemistry Atoms First 2e Openstax

Objective Test 2 On Quantum Numbers Mm 30 Time 45 Min

Solved 6 List All The Possible Quantum Numbers For An El Chegg Com
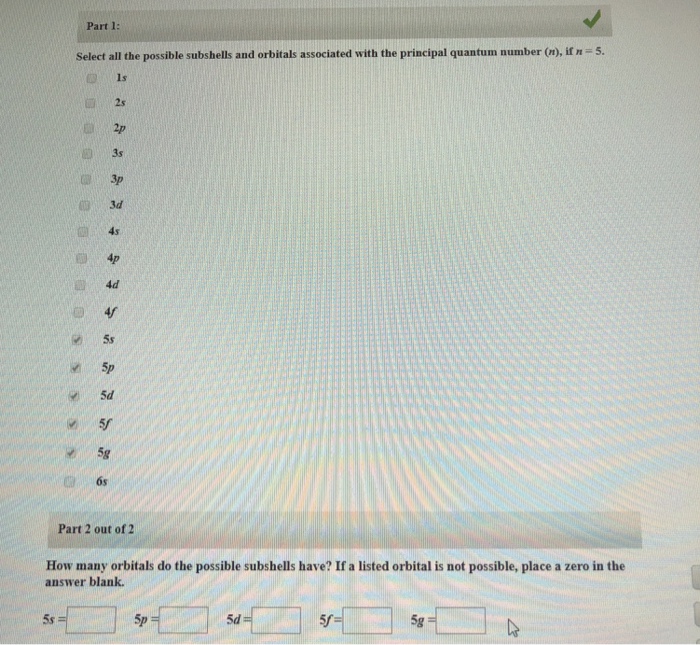
Solved Part 1 Select All The Possible Subshells And Orbi Chegg Com
New Pt Notation
Q Tbn 3aand9gcqefpif5c8gaczx7dlhc 01ks F0mszxq 8shsowu Dmcmze3vp Usqp Cau
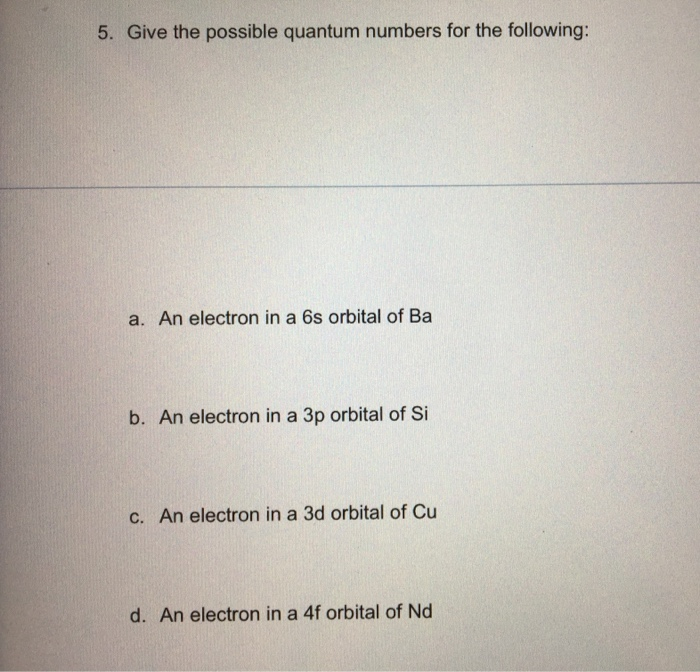
Solved 5 Give The Possible Quantum Numbers For The Follo Chegg Com

Energy Of Orbitals Chemistrygod

Worksheet 16

Quantum Numbers For The First Four Shells Video Khan Academy

Principal Quantum Number An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Many Electron Atoms And The Periodic Table Of Elements Absolutely Small How Quantum Theory Explains Our Everyday World Michael D Fayer

Quantum Numbers

Review Day Orbitals Are Described With 2 Different Numbers Called Quantum Numbers 1 Principal Quantum Number N Integer Values That Describe The Energy Ppt Download

Quantum Numbers
Www Philadelphia Edu Jo Academics Ajaber Uploads Ch 6 Quantum theory and the electronicstructure of atom Part3 Pdf

What Is The Orbital Angular Momentum Quantum Number For The Orbital 5p Socratic
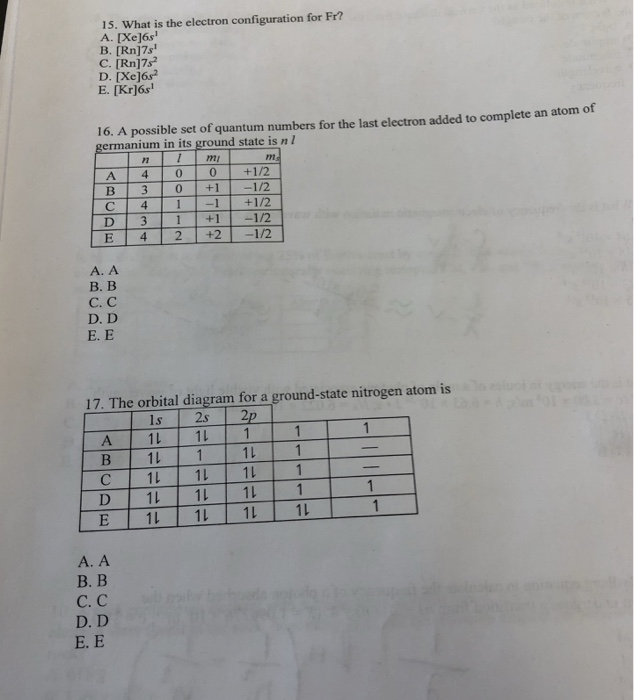
Solved 15 What Is The Electron Configuration For Fr B Chegg Com

Electron Configurations Ppt Download
Answers Electronic Structure

17 The Valence Electronic Configuration Of An Atom Is 6s It D Orbital Of The Penultimate Shell Contains Two Unpaired Electrons Calculate The Atomic Number A 72 B 48 C 76 D 58

Quantum Numbers Part Two Ppt Download
Chapter 2 Quantum Theory

Quantum Numbers Worksheet By Olivia Hunter Issuu

Answered Using A Noble Gas Notation Write The Bartleby

Energy Levels Of The S And D Orbitals In A Single Copper Silver And Download Scientific Diagram
New Pt Notation

Perspective Relativistic Effects The Journal Of Chemical Physics Vol 136 No 15

Which Element Has 18 Electrons In Its Outermost Shell Quora

What Are The Quantum Numbers Of Carbon Socratic

Electron Configurations How To Write Out The S P D F Electronic Arrangements Of Atoms Ions Periodic Table Oxidation States Using Orbital Notation Gce A Level Revision Notes
Q Tbn 3aand9gcqalnpzwaqwgjd5n9bwfajqft1hm U8awiv6rbrjmzvsum6mkym Usqp Cau

Quantum Numbers And Atomic Orbitals Atomic Orbital Angelo State

Tang 03 Quantum Numbers

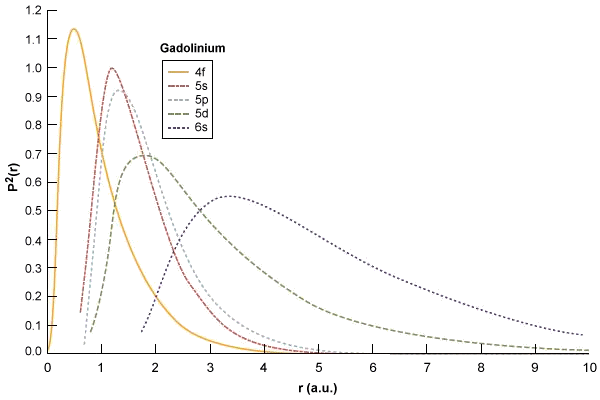
Square Of The Radial Wavefunctions For The 4f 5s 5p And 6s Energy Download Scientific Diagram

Radial Distribution Of The 6s And 7s All Electron And Download Scientific Diagram

Quantum Numbers Atomic Orbitals And Electron Configurations

Principal Quantum Number An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Building Up The Periodic Table

Electrons In Atoms 36 Electron Configuration Orbital Diagram And Quantum Numbers For W Youtube
Fafuizlwxm11m
Identify Which Sets Of Quantum Numbers Are Valid For An Electron Each Set Is Ordered N L Ml Ms Home Work Help Learn Cbse Forum

Quantum Numbers Chemistry Socratic

Color Online A The Pdos Of The Bi 6s Orbital Blue And Te 5p Download Scientific Diagram
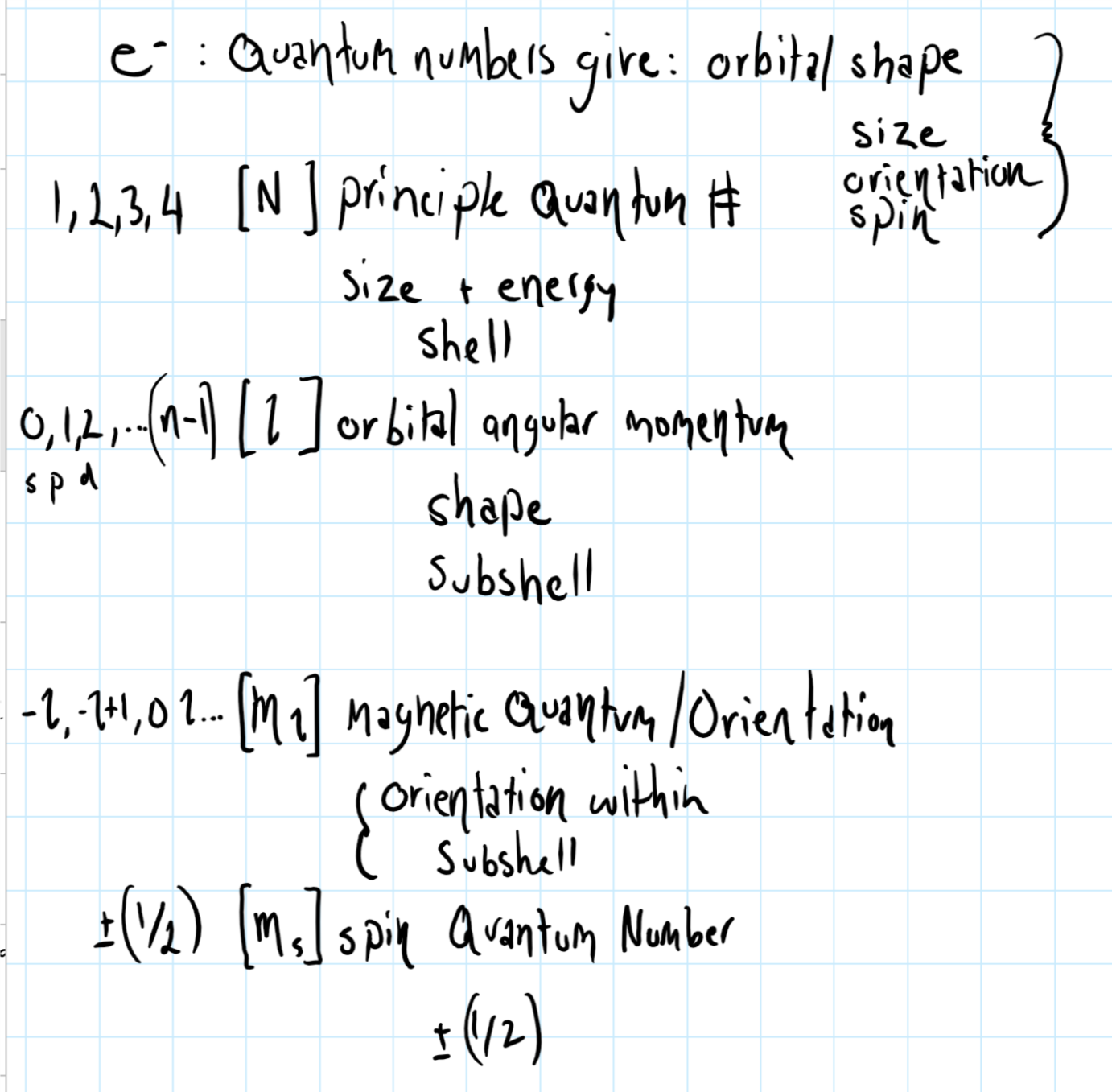
What Do The Four Quantum Numbers Describe About An Electron Socratic
11 10 The Schrodinger Wave Equation For The Hydrogen Atom Chemistry Libretexts

Which Of The Following Statements Is True Clutch Prep
Building Up The Periodic Table

Quantum Numbers
S P D F Obitals Notation Shapes Diagrams How To Work Out Electron Arrangements Configurations Order Of Filling Quantum Levels Electronic Structure Of Atoms Gce A Level Revision Notes
The Trouble With The Aufbau Principle Feature Rsc Education
Q Tbn 3aand9gctvfnhwgclwk Nkk4ojvliyaudem5vgicuvpk Czgq1di8dysru Usqp Cau
1 5 1 Quantum Numbers Worksheet Key
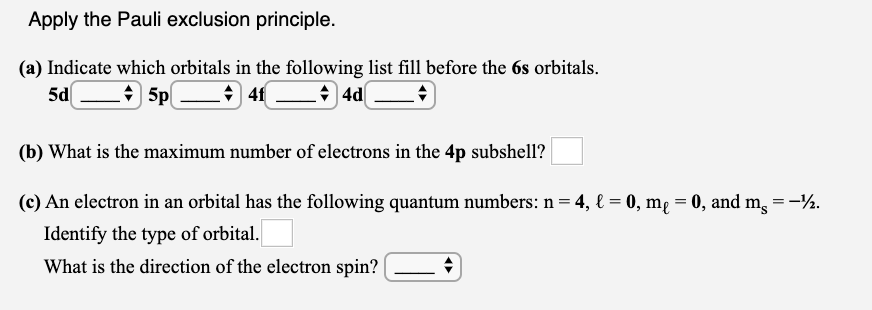
Solved Apply The Pauli Exclusion Principle A Indicate Chegg Com

Energy Of Orbitals Chemistrygod

Electron Configuration Wikipedia
Http Wwpsd Sharpschool Com Common Pages Displayfile Aspx Itemid

Ch 18 Electron Orbitals Classnotes

List The Sequence In Which The Following Orbitals Fill Up 1s 2s 3s 4s 5s 6s 7s 2p 3p 4p 5p 6p 7p 3d 4d 5d 6d 4f 5f Study Com

Quantum Numbers Video Quantum Physics Khan Academy

Atomic Orbital Wikipedia
Definition Of Sublevel Chemistry Dictionary

Quantum Electron Config Ps Answer Key

Solved A Gold Atom Has Electrons In Both The 6s Orbital A Chegg Com

Why Is Mercury A Liquid Pcbpedia
Q Tbn 3aand9gcseyobbyyxbjn6tvzukgg8pqxexr4l9yuq G9cwemw2k9xszngu Usqp Cau



